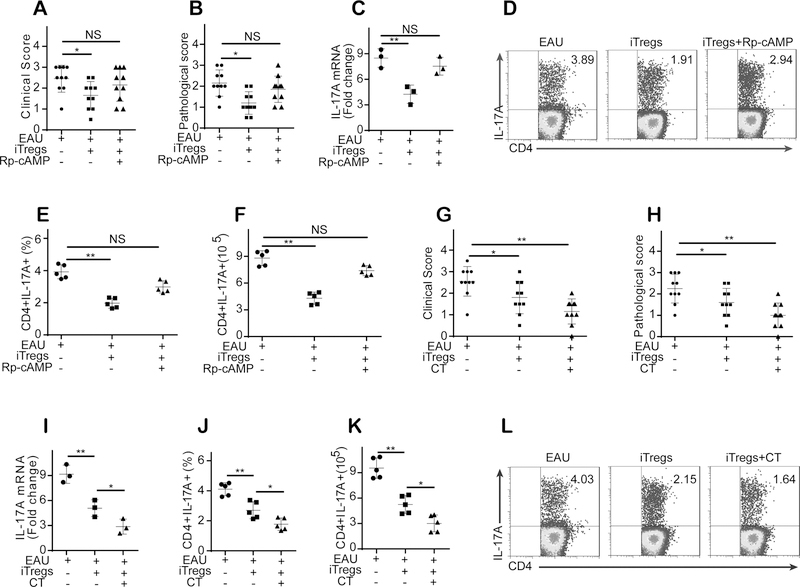
Figure 7. cAMP is critical for iTreg-mediated amelioration of established EAU, and increasing the intracellular cAMP level in iTregs before transfer enhanced their therapeutic effects on established EAU.
(A-B): iTregs pretreated with Rp-cAMPS did not attenuate EAU in mice (n = 10). (C-F): The preincubation of iTregs with Rp-cAMPS significantly decreased their capability to inhibit IL-17 expression and decreased the number and frequency of CD4+CD17A+ T cells in mice with EAU (n = 6). (G-H): The pretreatment of iTregs with CT, which increases the intracellular cAMP level in iTregs, improved the therapeutic effects of iTregs on EAU in mice (n = 6). (I-L): CT pretreatment improved iTregs’ capability to inhibit IL-17 expression and decreased the number and frequency of CD4+CD17A+ T cells in EAU mice (n = 3, gated on CD4). The results were representative of three independent experiments. The data are presented as the means ± SDs. NS: P > 0.05; *: P <0.05; **P <0.01 (between the indicated groups). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction.