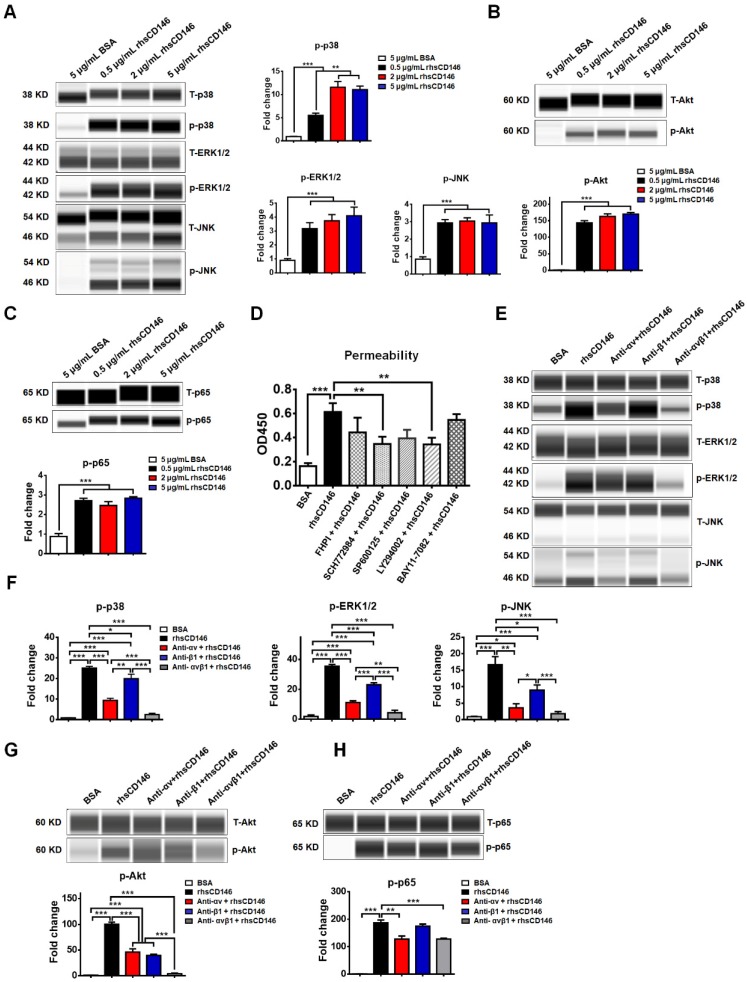
Figure 5.
MAPK, Akt and NF-кB signaling pathways are involved in sCD146-integrin αvβ1 induced hyperpermeability of hCMEC/D3 cells. (A-C) Phosphorylation of p38, ERK1/2, JNK, Akt and NF-кB was induced by treatment with 0.5, 2 or 5 μg/mL rhsCD146 for 10 min in hCMEC/D3 cells. At least three independent assays were performed. (D) MAPK, Akt and NF-кB signaling pathways are involved in sCD146-induced hyperpermeability of hCMEC/D3 cells. hCMEC/D3 cells were preincubated with signaling inhibitors 45 min before treatment with 5 μg/mL rhsCD146. The working concentration of signaling inhibitor of p38 (FHPI), JNK (SP600125), and NF-кB (BAY11-7082) is 10 μM, of ERK1/2 (SCH772984) is 2 μM and of Akt (LY294002) is 5 μM. (E-H) rhsCD146-induced phosphorylation of p38, ERK1/2, JNK, Akt and NF-кB was inhibited by anti-integrin αv and β1 antibodies. hCMEC/D3 cells were preincubated with 3 μg/mL IgG, anti-integrin αv, anti-integrinβ1 or anti-integrin αvβ1 antibodies for 30 min, and then, 5 μg/mL BSA or rhsCD146 was added to the culture medium and incubated for another 10 min. The cell lysates were harvested for western blot analysis.