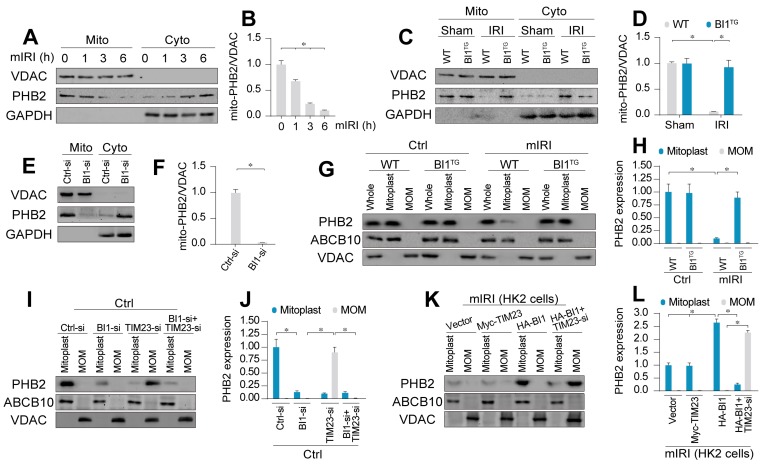
Figure 3.
BI1 promotes import of PHB2 into mitochondria. (A-B) In vitro, after different times of IRI, proteins were isolated from tubule cells. Then, mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions were collected. PHB2 expression was determined using Western blots. VDAC was employed as the loading control for mitochondrial fraction whereas GAPDH was used as the marker of cytosolic fraction. (C-D) In vivo, proteins were isolated from reperfused kidney and mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions were collected. PHB2 expression was determined using Western blots. VDAC was utilized as the loading control for mitochondrial fraction whereas GAPDH was employed as the marker of cytosolic fraction. (E-F) siRNA against BI1 (BI1-si) and control siRNA (Ctrl-si) were transfected into primary tubule cells and then the expression of mitochondrial PHB2 (mito-PHB2) was determined. (G-H) In primary tubule cells from BI1TG and WT mice, whole mitochondrial fraction (Whole) was firstly isolated and then mitochondrial outer-membrane (MOM) and mitoplast (inner-membrane plus matrix) fractions were collected. Western blotting was used to analyze the expression of PHB2 in whole, mitoplast and MOM fractions. ABCB10 was utilized as a loading control for mitoplast whereas VDAC was used as a MOM marker. (I-J) Under normal condition, BI1 siRNA (BI1-si), TIM23 siRNA (TIM23-si) and control siRNA (Ctrl-si) were transfected into primary tubule cells. Then, levels of PHB2 were determined. (K-L) Under mIRI condition, Myc-TIM23, HA-BI1 and vector were transfected into HK2 cells. Moreover, TIM23-si was employed to silence TIM23 in HK2 cells infected with HA-BI1 prior to determination of PHB2. Experiments were repeated for at least three times and data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 6 mice or 3 independent cell isolations per group). *p<0.05.