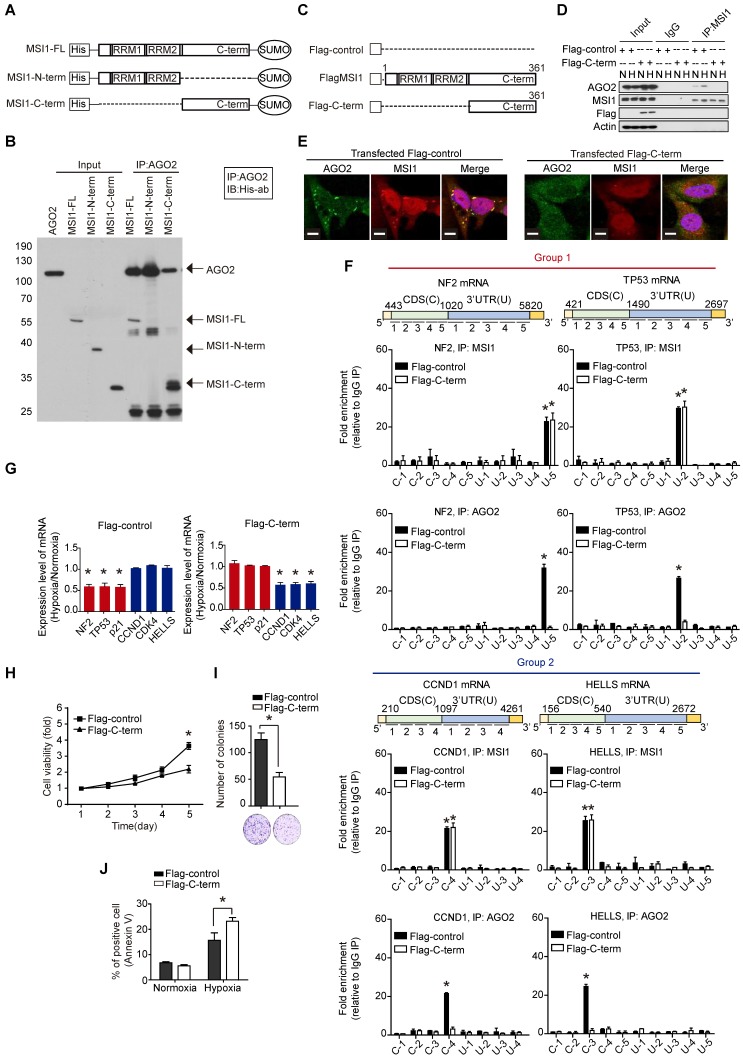
Figure 6.
The C-terminal of MSI1 is critical for AGO2 binding and cell viability. (A) Schematic presentation of the constructs of full-length, C-terminus, and N-terminus of MSI1 as well as wild-type AGO2 for purifying recombinant proteins. (B) Pull-down assay with recombinant MSI1 and AGO2 proteins showed that the C-terminus of MSI1 is essential for the direct MSI1/AGO2 interaction. (C) A Schematic illustrating the Flag-control, full-length and C-terminal (C-term) fragment of human MSI1. The construct of MSI1 C-term was sub-cloned into p-3×Flag-Myc-CMV expression vector. (D) Cells transient transfected with Flag-control or Flag-tagged MSI1 C-term (Flag-C-term) were subjected to co-immunoprecipitation assay for endogenous AGO2 and MSI1 protein-protein interaction. Transfection of the Flag-C-term blocked hypoxia-induced MSI1/AGO2 binding. (E) Cells transfected with Flag-control or Flag-C-term were analyzed under confocal microscopy for the subcellular co-localization of MSI1 (Red) and AGO2 (Green). (F) Flag-control and Flag-C-term transfected cells were subjected to an modified-RIP assay using anti-MSI1 or anti-AGO2 antibodies, followed by RNA fragmentation and qRT-PCR analysis to determine the fold change enrichment of the coding sequence (CDS) and 3´ UTR of the NF2, TP53, CCND1 and HELLS mRNAs. Quantification of the fold changes of binding signals was performed by normalizing IP signals to IgG-precipitated controls. The peaks indicated MSI1 or AGO2 palindromic-binding sequence. Flag-C-term blocked the binding of AGO2 but not MSI1 to target sequence in mRNAs. (G) Flag-control and Flag-C-term transfected cells were subjected to normoxia or hypoxia for 24 hr. Purified total RNA was subjected to RT-PCR using primers specific for NF2, TP53, CDKN1A, CCND1, CDK4, and HELLS. The mRNA levels under hypoxia were normalized with that under normoxia and presented as relative fold changes in the chart. (H) 05MG cells transiently transfected with Flag control or Flag-tagged MSI1 C-term were subjected to an MTT viability assay. The relative fold change of the number of viable cells in each day was presented in the graph. (I) Flag-control and Flag-C-term transfected cells were subjected to colony formation assay for 10 days and quantitated by ImageJ software. (J) The percentage of apoptotic cells of Flag-control and Flag-C-term transfected cells was determined by external Annexin-V under normoxiac and hypoxic conditions.