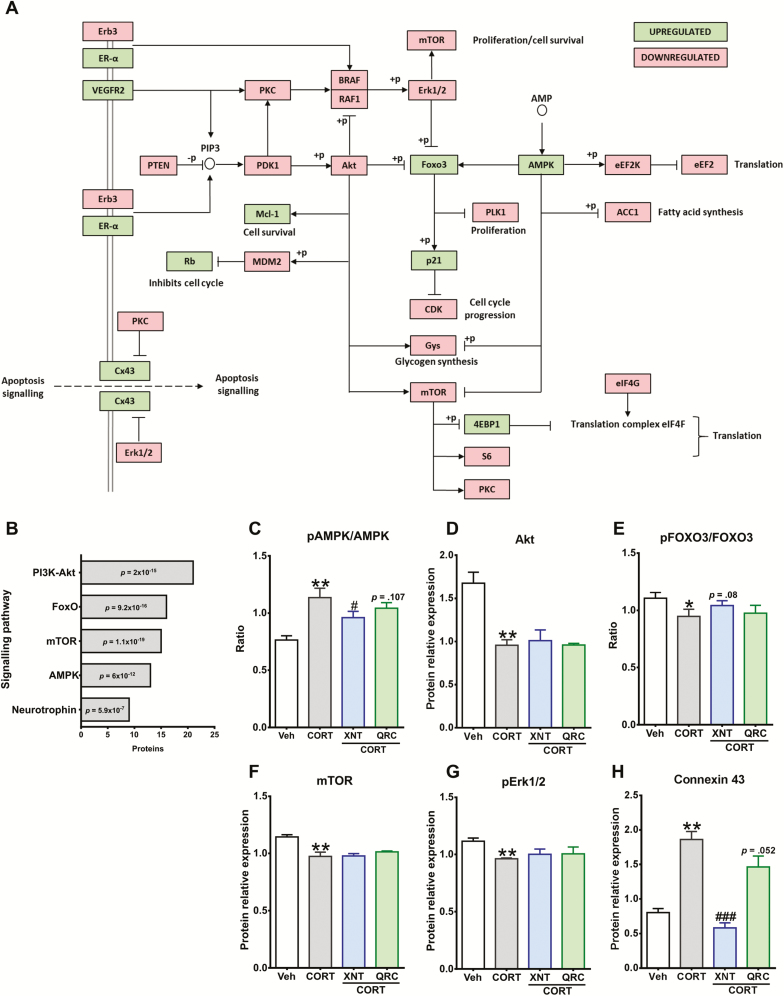
Figure 5.
Impact of xanthohumol and quercetin on corticosterone (CORT)-induced changes in Akt/mTOR, AMPK, and Erk1/2 signaling pathways. (A) Schematic interaction map of proteins altered by CORT; upregulated expression of proteins is shown in green and downregulated proteins are highlighted in red. Cortical cells were treated with 200 µM CORT for 96 hours. The relative expression of proteins involved in proliferation, cell growth and apoptosis was determined using the reverse-phase protein array (RPPA) approach. (B) Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) signaling pathways affected by CORT were detected using the functional annotation tool DAVID 6.8. (C–H) After 24-hour exposure to 5 µM xanthohumol or 3 µM quercetin, cortical cells were treated for 96 hours with 200 µM CORT. The levels of protein expression of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), protein kinase B (Akt), forkhead box O3 (FOXO3), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 (Erk1/2), and connexin 43 were quantitatively measured using RPPA and provided by MD Anderson. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments (***P < .001; **P < .01; *P < .05 vs vehicle groups; ###P < .001; #P < .05 vs CORT groups).