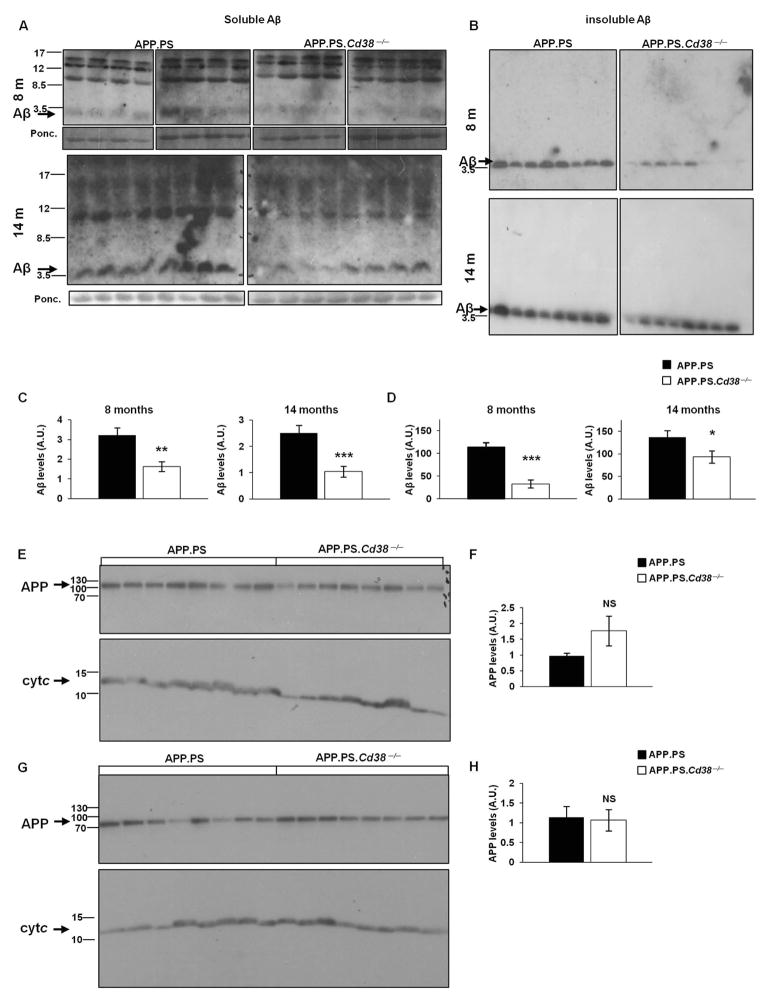
Figure 2. Loss of CD38 reduces soluble and insoluble Aβ peptide but not APP levels in APP.PS mice.
(A,B) Immunoblot analysis of Aβ peptide levels. Soluble (A) and insoluble (B) protein extracts were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. Proteins (175 and 2 μg for soluble and insoluble respectively) were separated by SDS-PAGE and membranes were probed with anti-Aβ Abs. Aβ levels in the soluble fraction were normalized to a ~12 KDa band in the Ponceau staining (lower panels). (C, D) Quantification of immunoblot results of soluble (C) and insoluble (D) Aβ levels (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005, Student’s t test). (n = 8). (E, G) Immunoblot analysis of APP levels. Cortical protein extracts were prepared from brains of APP.PS and APP.PS.Cd38−/− mice at 8 (E) and 14 (G) months of age. Proteins (50 μg) were separated on SDS-PAGE and membranes were probed with anti-APP Abs as described in Materials and Methods. The membranes were cut into two parts and each part was stained separately for either APP or for cytochrome c for normalization. APP levels were normalized to cytochrome c (Cyt c). (F, H) Quantification of APP immunoblot results at 8 (F) and 14 (H) months of age. (NS, not significant; Student’s t test) The quantified values shown are presented as the mean ± SEM (bars). (n = 8 for each genotype).