Figure 3.
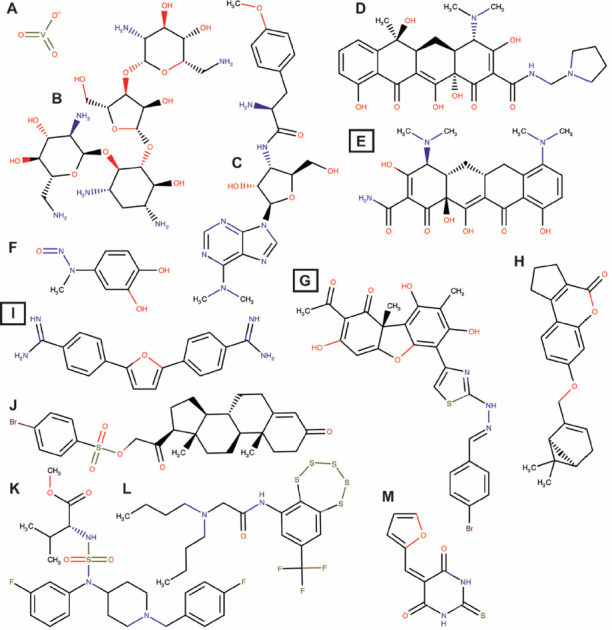
Structures of potential Tdp1 inhibitors. A: Vanadate; B: Neomycin; C: Puromycin; D: Rolitetracycline; E: Minocycline; F: methyl-3,4-dephostatin; G: (R,E)-2-acetyl-6-(2-(2-(4-bromobenzyliden)hydrazinyl)thiazole-4-yl)-3,7,9-trihydroxy-8,9b-dimethyl dibenzo[b,d]furan-1(9bH)-one; H: 7-(((1S,5R)-6,6-Dimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-en-2-yl)methoxy)-2,3-dihydrocyclopenta[c]chromen-4(1H)-one; J: 3,20-Dioxopregn-4-en-21-yl 4-bromobenzenesulfonate; K: 2-(Dibutylamino)-N-(8-(trifluoromethyl)benzo[f]-[1,2,3,4,5] pentathiepin-6-yl)acetamide; L: (R)-Methyl 2-(N-(1-(4-fluorobenzyl)piperidin-4-yl)-N-(3-fluorophenyl) sulfamoyl amino)-3-methylbutanoate; M: 5-(2-Furyl Methylidene)-2-thioxo hexahydro pyrimidine-4,6-dione. Box letters are compounds tested in vivo. Chemical structures were drawn using MarvinSketch (17.3.13.0) ChemAxon (http://www.chemaxon.com)
