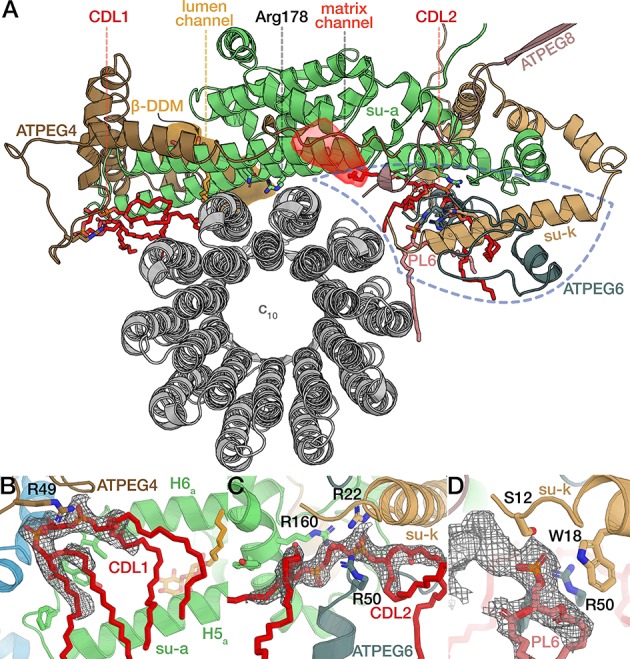
Figure 5. The rotor-stator interface is flanked by bound cardiolipin.
(A) View from the c-ring towards the membrane-embedded stator subunits. H5a and H6a are augmented by the tilted, amphipathic H1EG4 (brown). Cardiolipin molecules flanking subunit a are shown in red (tails of acyl chains are mostly disordered and shown only for illustration). Proton half-channels on the lumen and matrix side are shown in orange and red respectively. Remaining subunits not shown for clarity. The conserved R178 and the H186 at the lumen channel exit are shown with interacting residues. (B) Entrance of the lumenal channel (orange) is lined by the termini of subunit f, ATPEG4, subunit 8, ATPEG3, as well as a lumenal segment of subunit i/j. Inside the Fo, the lumen channel is confined by transmembrane helices of subunits f and b. β-DDM occupying the exit of the lumen channel shown in orange with density map as mesh, c-ring in grey. Arrows indicate proposed path of proton flow. (C) Polar and protonatable residues between R178 and the matrix-side half channel (red mesh). Subunit k contributes a horizontal helix (H1k) to the rotor-stator interface.
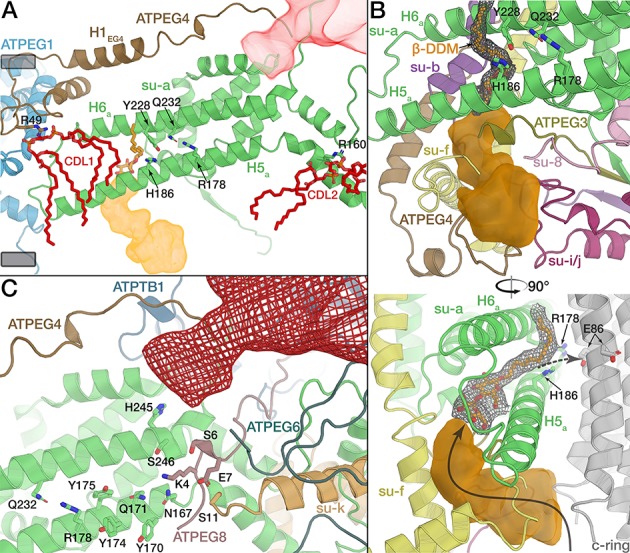
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Comparison between E. gracilis and S. cerevisiae rotor-stator interfaces.
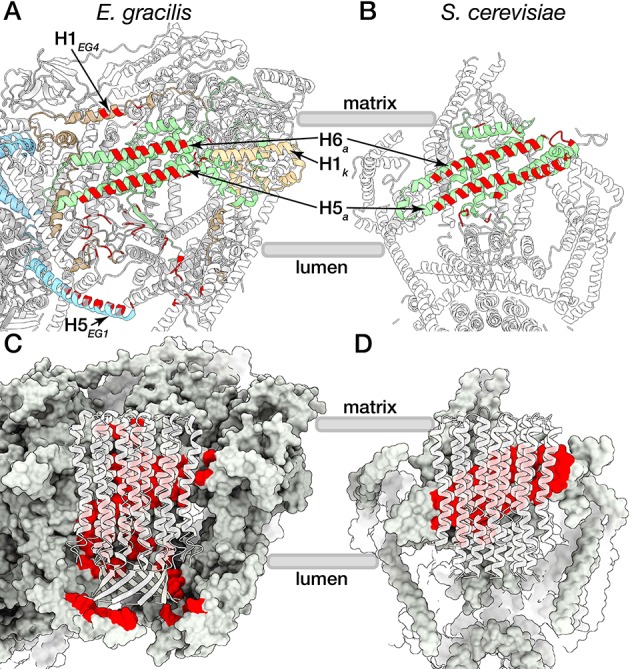
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. Native phospholipids of the rotor-stator interface.