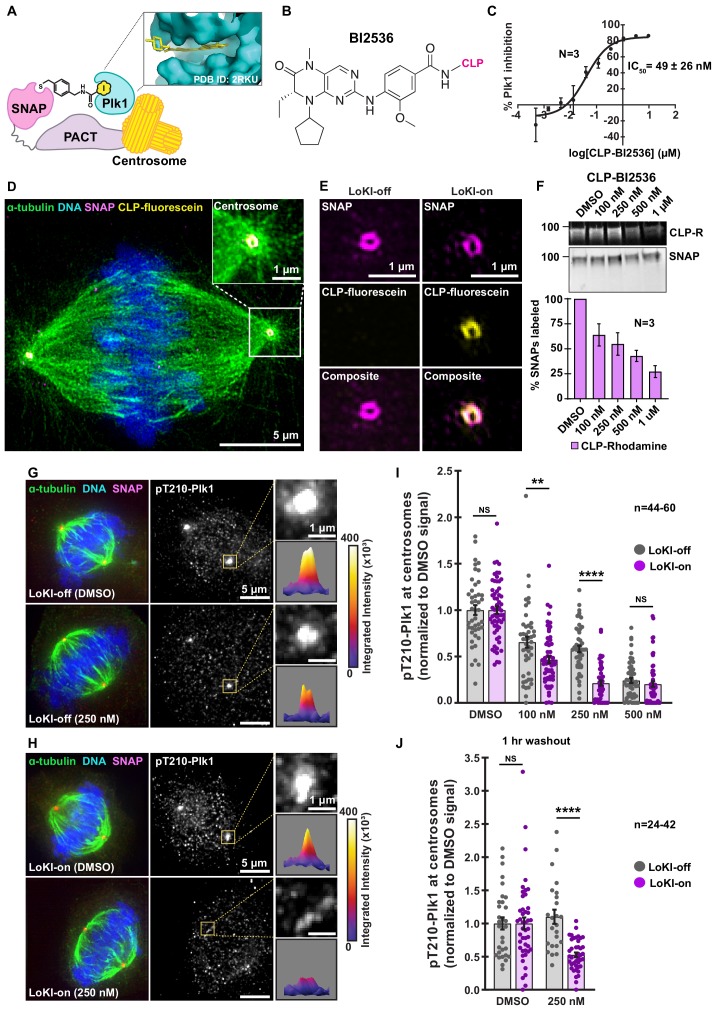
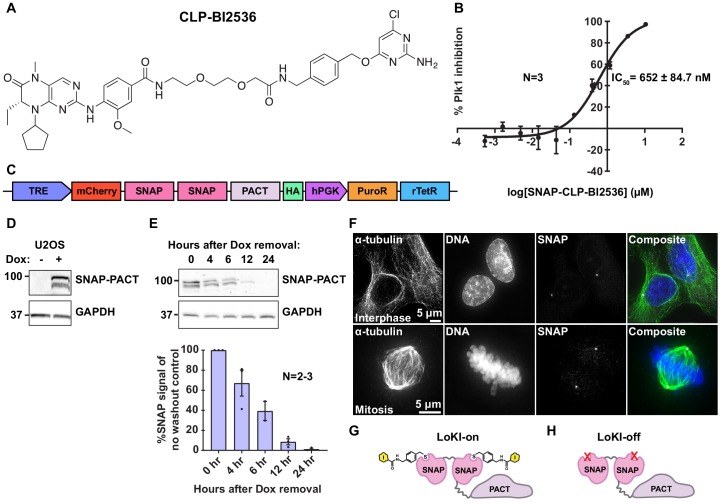
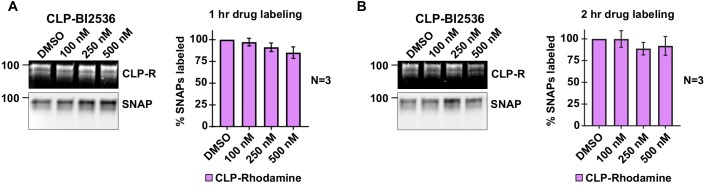
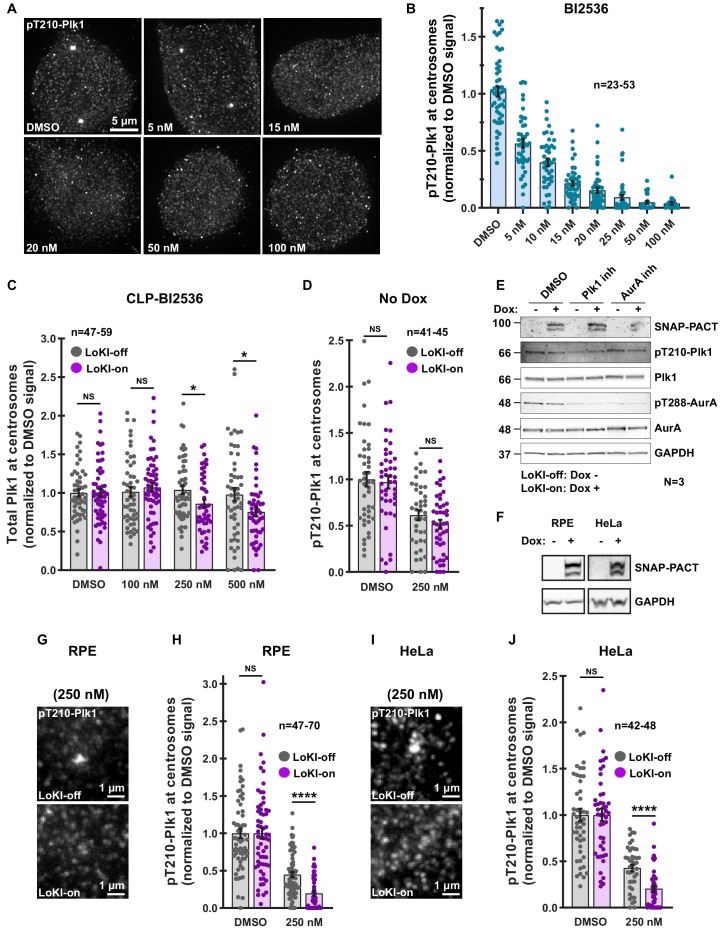
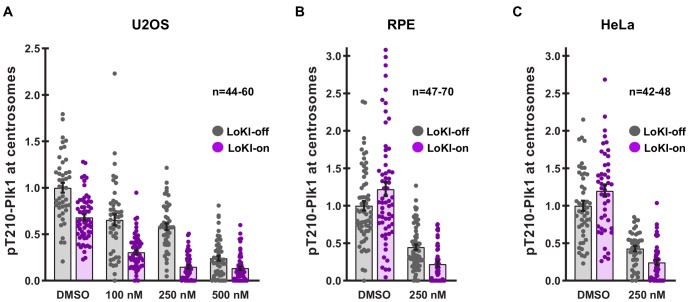
Figure 2. Validation of the LoKI platform.
(A) Schematic of a centrosome-directed LoKI platform. SNAP-PACT fusion proteins conjugate CLP-linked Plk1 inhibitors at centrosomes. Inset depicts BI2536 in the ATP-binding pocket of Plk1. (B) Chemical structure of CLP-BI2536. (C) Dose-response curve of in vitro Plk1 inhibition with CLP-BI2536. (D) Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) of a LoKI-on U2OS cell labeled with CLP-fluorescein. Immunofluorescent detection of α-tubulin (green), DNA (blue), mCherry-SNAP-PACT (magenta) and CLP-fluorescein (yellow). Magnification of SNAP and CLP-fluorescein co-distribution at a centrosome (inset). (E) SIM micrographs of LoKI-off (left) and LoKI-on (right) U2OS cells. SNAP expression (top, magenta), CLP-fluorescein conjugation (mid, yellow) and composite images (bottom) are depicted. (F) Pulse-chase experiments measuring CLP-BI2536’s ability to block CLP-rhodamine conjugation to LoKI-on. In-gel rhodamine fluorescence (top), immunoblot of SNAP loading controls (mid), and fluorescence quantification of pulse-chase experiments (bottom). (G, H) Immunofluorescence of representative mitotic LoKI-off (G) and LoKI-on (H) U2OS cells treated with DMSO or 250 nM CLP-BI2536 for 4 hr. Composite images (left) show α-tubulin (green), DNA (blue), and SNAP (magenta). Immunofluorescent detection of pT210-Plk1 (mid, gray) as an index of kinase activity. 5X magnification of centrosomal pT210-Plk1 signals and surface plots measuring integrated intensity of pT210-Plk1 signal (insets). (I, J) Quantification of centrosomal pT210-Plk1 immunofluorescence for LoKI-expressing cells. Points represent individual cells (n). Data normalized to DMSO. Application of DMSO or CLP-BI2536 for 4 hr, (I) 100 nM, LoKI-off, n = 46, LoKI-on, n = 59, **p=0.0059; 250 nM, LoKI-off, n = 46, LoKI-on, n = 46, ****p<0.0001 and drug treatment followed by 1 hr washout (J) 250 nM, LoKI-off, n = 24, LoKI-on, n = 42, ****p<0.0001. Experiments were conducted at least three times (N = 3) and P values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Data are mean ± s.e.m. NS, not significant. Source files for analysis of pulse-chase experiments are available in Figure 2—source data 1 and for quantification of pT210-Plk1 are available in Figure 2—source data 2.