FIGURE 1.
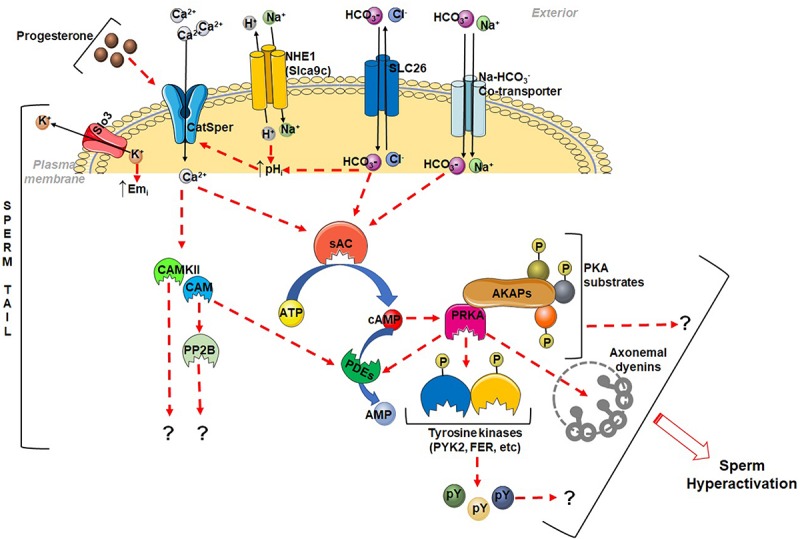
Schematic diagram showing some of the signaling events during sperm hyperactivation. CatSper channels are activated either by progesterone or alkalization of sperm cytosol to permit calcium entry. The Cl––HCO3– exchanger, SLC26A3 and the Na+–HCO3– co-transporter, and Na+–H+ exchanger, NHE1 (Slca9c), aid in alkalization of sperm pHi. Slo3 K+-channels are activated by alkalization and causes hyperpolarization. Both Ca2+ and HCO3– stimulate sperm sAC to increase cAMP levels. Cyclic AMP, in turn activates sperm PKA (PRKA), which is expected to phosphorylate several substrates including protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). Ca2+ also activates calmodulin (CAM) and calmodulin dependent phosphatase, calcineurin (PP2B) and a protein kinase CAMKII. The downstream effect and mechanism of action of these enzymes in promoting sperm fertilization is not well understood. Index: dotted arrow indicates activation, upward arrow denotes increase, and question mark (?) indicates unknown mechanism.
