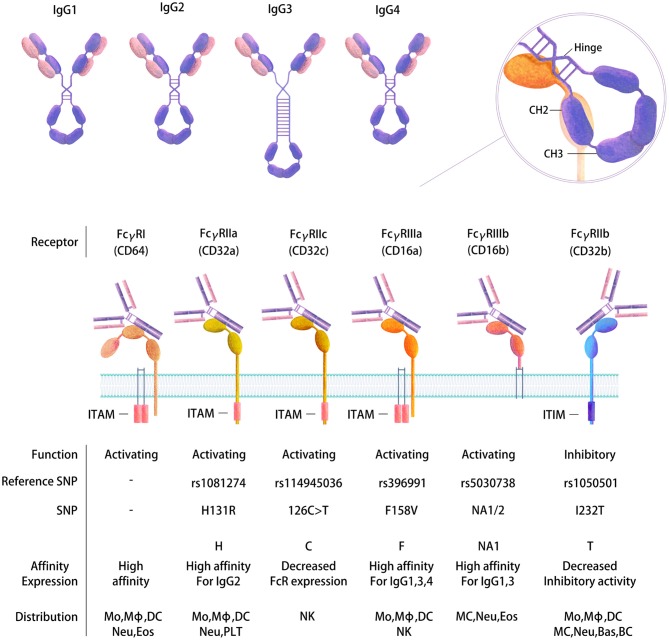
Figure 2.
Human FcγR gene polymorphisms and the expression and affinity of IgG subtypes. Four IgG subtypes are present in human serum that have distinct structures and functions (top). FcγRs belong to the Ig receptor superfamily and comprise two or three extracellular Ig domains that mediate IgG binding. Differential immune regulatory effects are produced depending on binding to FcRs. Activating or inhibitory functions occur based on the presence of an intracellular cytoplasmic domain ITAM or ITIM motif that transduces an immunostimulatory or inhibitory signal, respectively, following receptor cross-linking. Binding of the Fc to the receptors is mediated at the CH2-CH3 interface following a conformational change (right). The diversity of FcγRs is further increased by SNPs in their extracellular domains, which in turn affect the expression of FcRs and their binding affinity and function (bottom). Mo, Monocyte; Mϕ, Macrophage; DC, Dendritic cell; MC, Mast cell; Neu, Neutrophil; Bas, Basophil; Eos, Eosinophil; NK, Natural killer cell; BC, B cell; PLT, Platelet.