Figure 1.
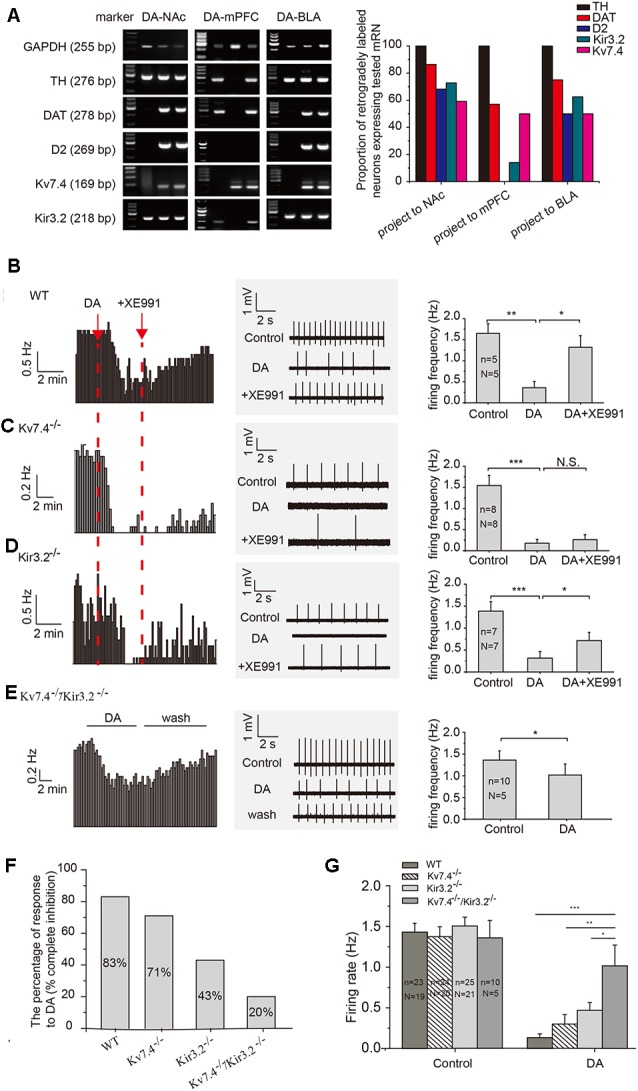
Kv7.4 contribute to the dopamine (DA)-induced inhibition of NAc-projecting DA neuron firing. (A) Single-cell polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis in retrogradely labeled ventral tegmental area (VTA) DA neurons from different projections. (B–D) VTA DA neuron firing recorded with loose cell-attached patch recordings. XE991 (3 μM), a Kv7 blocker, reversed the DA-induced inhibition of neuron firing in WT (B) and Kir3.2−/− (D) mice, but not in Kv7.4−/− mice (C). (E) The effect of DA on spontaneous firing in DA neurons from Kv7.4−/−/Kir3.2−/− mice. (F) The percentage of VTA-NAc DA neurons with firing rate being inhibited to less than 20% (complete inhibition) in WT, Kv7.4−/−, Kir3.2−/− and Kv7.4−/−/Kir3.2−/− mice. (G) Average DA inhibition on firing rate in all recorded VTA-NAc DA neurons from WT, Kv7.4−/−, Kir3.2−/− and Kv7.4−/−/Kir3.2−/− mice. One-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05; N.S., not significant. One-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. N, number of animals; n, number of recordings.
