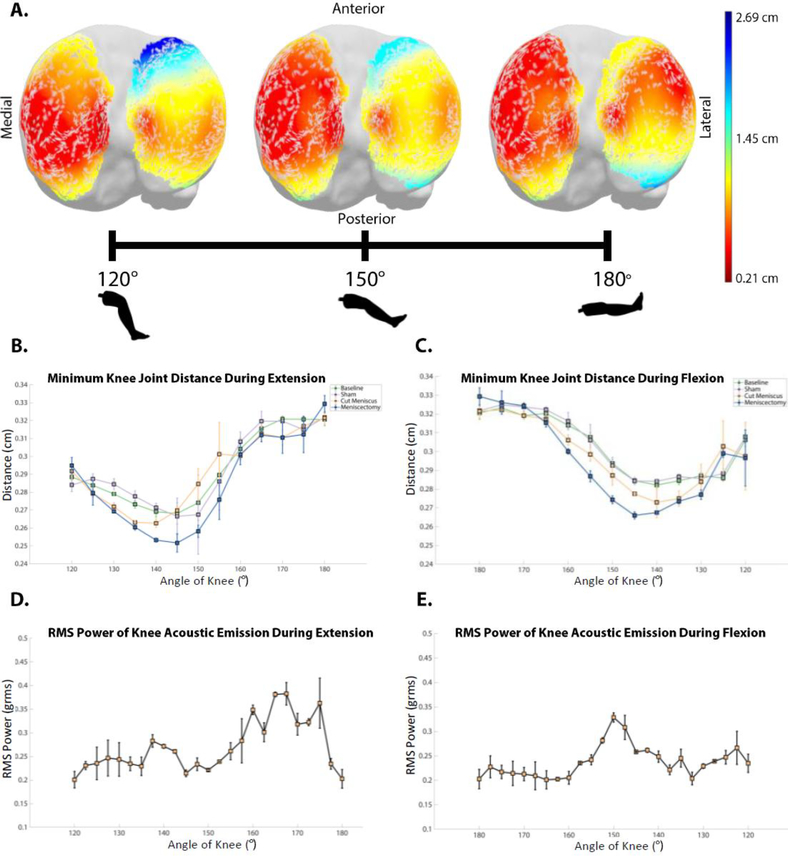
Fig 5. Comparison of tibiofemoral distances to sound recordings during a flexion-extension cycle.
(A) Heatmap of distances from femoral condyles to tibial plateau at select distances (i.e. 120°, 150°, 180°). These heatmaps appeared nearly identical during flexion and extension. Minimum tibiofemoral distances at each degree of movement during (B) extension and (C) flexion (Error bars indicate one standard deviation from the mean of three trials at each data point). In B and C, the 1000 nearest vertices of the 7076 total vertices creating the 3D mesh are averaged with their standard deviations displayed. RMS Power of the joint acoustic emissions at each degree of movement during (D) extension and (E) flexion (Error bars indicate one standard deviation from the mean of the AEs of all n=9 cadaver legs tested.).