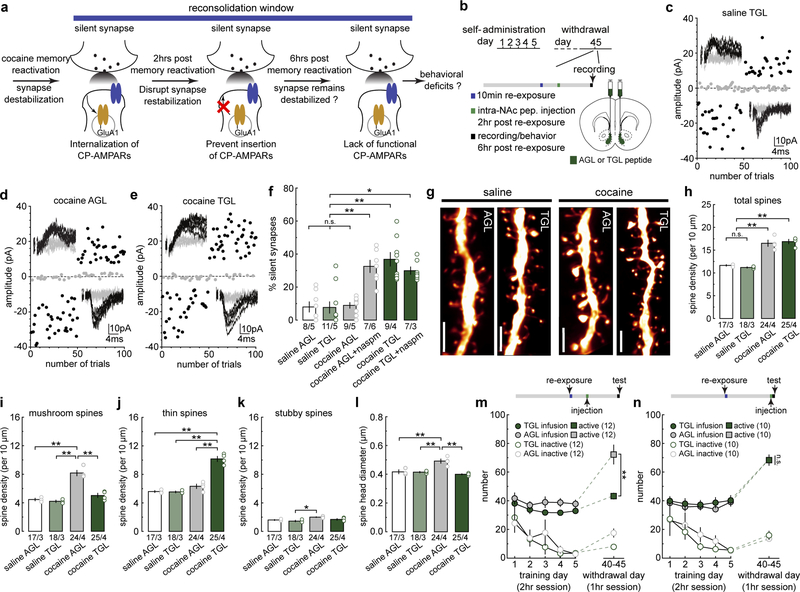
Figure 3. Synapse re-silencing destabilizes cocaine memories.
(a) Diagram illustrating the hypothesis that preventing CP-AMPAR re-insertion during the reconsolidation window locks cocaine-generated synapses in the silent state and compromises cue-induced cocaine seeking.
(b) Diagram showing experimental timeline.
(d-e) Example EPSCs evoked at −70 mV and +50 mV by minimal stimulation (insets) over 100 trials from saline- or cocaine-trained rats with NAcSh TGL infusion and the effects of naspm.
(f) Summary showing that while intra-NAcSh TGL or AGL did not affect the % silent synapses in saline-trained rats, intra-NAcSh TGL, but not AGL, maintained the cue re-exposure-induced high % silent synapses in cocaine-trained rats beyond the presumable 6-hr destabilization window, and CP-AMPAR inhibition by naspm did not further affect the % silent synapses (saline AGL = 6.40 ± 3.68, n = 5 animals; saline TGL = 7.06 ± 3.07, n = 5 animals; cocaine AGL = 9.70 ± 1.05, n = 5 animals; cocaine AGL naspm = 33.76 ± 3.71, n = 6 animals; cocaine TGL = 37.10 ± 3.71, n = 4 animals; cocaine TGL naspm = 29.70 ± 3.08, n = 3 animals, F5,22=14.85, p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA; n.s. > 0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Bonferroni posttest).
(g) Example NAcSh dendrites from saline-trained rats and cocaine-trained rats with AGL and TGL infusions. Scale bar, 2.5 μm.
(h) Summary showing the density of total spines was increased in cocaine-trained rats with either AGL or TGL compared to saline-trained rats (saline AGL = 11.66 ± 0.171, n = 3 animals; saline TGL = 11.20 ± 0.146, n =3 animals; cocaine AGL = 16.52 ± 0.69, n =4 animals; cocaine TGL = 16.89 ± 0.488, n = 4 animals, F3,10,=36.01, p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA; n.s.>0.05 **p<0.01, Bonferroni posttest).
(i) Summary showing the density of mushroom-like spines was increased in cocaine-trained rats with AGL compared to saline-trained rats, while TGL treatment normalized mushroom-like spine density to saline levels (saline AGL = 4.46 ± 0.19, n = 3 animals; saline TGL = 4.23 ± 0.163, n = 3 animals; cocaine AGL = 8.18 ± 0.383, n = 4 animals; cocaine TGL = 5.04 ± 0.302, n = 4 animals, F3,10=38.59, p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA; **p<0.01, Bonferroni posttest).
(j) Summary showing the density of thin spines was significantly increased in cocaine-trained TGL rats compared to cocaine-trained AGL rats or saline-trained rats (saline AGL = 5.60 ± 0.148, n = 3 animals; saline TGL = 5.54 ± 0.132, n = 3 animals; cocaine AGL = 6.33 ± 0.309, n = 4 animals; cocaine TGL = 10.16 ± 0.363, n = 4 animals, F3,10=60.80, p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA; **p<0.01, Bonferroni posttest).
(k) Summary showing densities of stubby spines in saline- and cocaine-trained rats with AGL or TGL treatment (saline AGL = 1.60 ± 0.076, n = 3 animals; saline TGL = 1.45 ± 0.117, n = 3 animals; cocaine AGL = 2.01 ± 0.051 n = 4 animals; cocaine TGL = 1.69 ± 0.118, n = 4 animals, F3,10=6.32, p=0.0112, one-way ANOVA; *p<0.05, Bonferroni posttest).
(l) Summary showing the mean spine head diameter was increased in cocaine-trained AGL rats compared to saline-trained rats, while TGL treatment normalized this increase to saline control levels (saline AGL = 0.417 ± 0.013, n = 3 animals; saline TGL = 0.415 ± 0.005, n = 3 animals; cocaine AGL = 0.492 ± 0.015, n = 4 animals; cocaine TGL = 0.400 ± 0.004, n = 4 animals, F3,10=16.17, p=0.0004, one-way ANOVA; **p<0.01, Bonferroni posttest).
(m) Summary showing that intra-NAcSh infusion of TGL, but not AGL, at 2hr after cue re-exposure decreased cue-induced cocaine seeking in cocaine-trained rats, measured 6 hr after cue re-exposure (AGL active = 72.25 ± 6.68, n = 12 animals; TGL active = 43.25 ± 2.07, n = 12 animals; AGL inactive = 17.58 ± 2.90, n =12 animals; TGL inactive = 7.92 ± 1.34, n =12 animals, F1,22=12.26, p=0.002, RM two-way ANOVA, withdrawal day 45 peptide x lever interaction; **p<0.01, Bonferroni posttest).
(n) Summary showing that rats with intra-NAcSh infusion of TGL 6 hr after cue re-exposure exhibited similar cue-induced cocaine seeking as AGL rats measured 6.5 hr after cue re-exposure (AGL active = 68.20 ± 2.87, n = 10 animals; TGL active = 68.20 ± 3.74, n =10 animals; AGL inactive = 13.30 ± 1.69, n = 10 animals; TGL inactive = 15.70 ± 2.94, n = 10 animals, F1,18=0.23, p=0.64, RM two-way ANOVA, withdrawal day 45 peptide x lever interaction). See Supplemental Table 1 for exact p values for all comparisons made during posthoc tests. Data presented as mean±SEM.