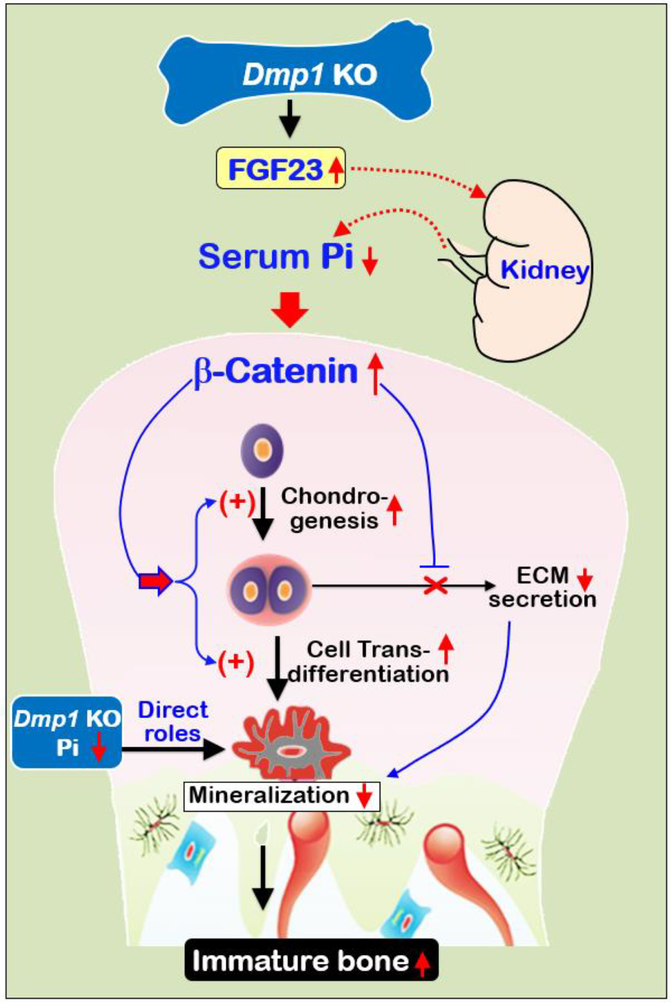
Fig. 9. Working hypotheses.
Removing Dmp1, a key ECM molecule released from osteocytes, leads to hypophosphatemia via an increase in FGF23 [5] (Fig. S2). Due to a lack of vasculi in cartilage, a low Pi particularly affects condylar chondrogenesis, leading to a sharp increase in β-catenin in chondrocytes. As a result, both chondrogenesis and cell trans-differentiation from chondrocytes to bone cells are significantly accelerated. However, the increased bone cells remain immature and the KO bone is poorly mineralized due to the direct role of a low Pi (for mineral formation) and a lack of DMP1 (for cell maturation), as well as a reduction in secretions of ECM (where mineral is deposited) caused by the increased β-catenin.