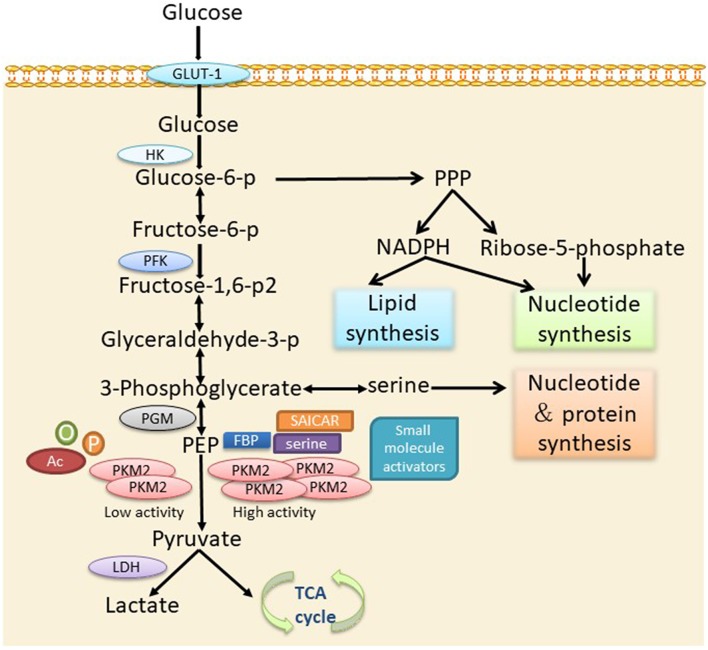
Figure 1.
The role of PKM2 in cellular metabolism via the glycolytic pathway. PKM2 is converted into an active tetramer under activation by serine, FBP, SAICAR, or small molecules, which promotes the conversion of PEP into pyruvate. Pyruvate enters the TCA cycle of the mitochondria and produces ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. In the absence of allosteric activators or post-transcriptional modifications, PKM2 presents mainly in an inactive dimer form, leading to the accumulation of glycolytic intermediates to meet the needs of the biosynthetic precursors of activated or proliferating cells. p, phosphorylation; Ac, acetylation; o, oxidation.