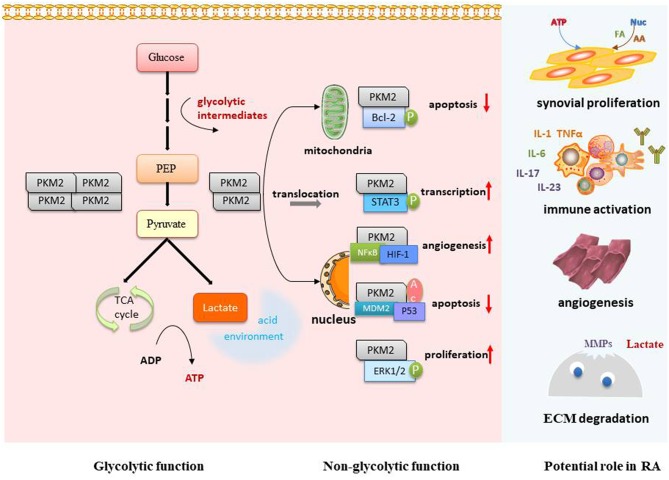
Figure 2.
Potential role and mechanism of PKM2 in RA. PKM2 can optimize the supply of energy and synthetic substrates for proliferative synoviocytes and activated immune cells via its glycolytic regulation function. The dimer form of PKM2 can interact with important RA transcription factors, such as STAT3, Bcl-2, HIF-1, and Erk1/2, so as to further regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and immune activation. The local acidic microenvironment caused by increased glycolysis is favorable for synoviocyte invasion, MMP-1 activation, and angiogenesis. p, phosphorylation; Ac, acetylation; FA, fatty acid; AA, amino acid; Nuc, nucleotide; ECM, extracellular matrix.