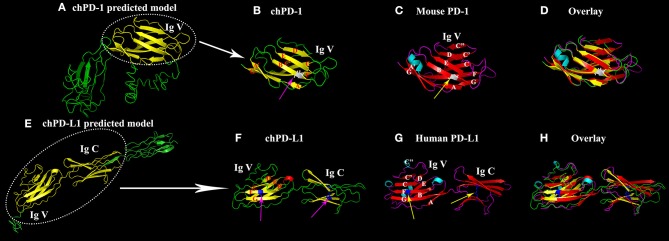
Figure 2.
Similarity of the Ig V domain of chPD-1 to the Ig V domain of mouse PD-1 and the Ig V and Ig C domains of chPD-L1 to the Ig V and Ig C domains of human PD-L1. (A,E) Predicted homology structural models of chPD-1 and chPD-L1 by I-TASSER software. Although difference in the number of presence of β sheets, the overall structures have identical orientations. (B–D) Overlay of Ig V domains of chPD-1 with Ig V mouse PD-1. (B) The Ig V domain of chPD-1 is shown in yellow, and (C) the Ig V domain mouse PD-1 is shown in red. In mouse PD-1, the two β-sheets are labeled A'GFCC'C” and ABED. In chPD-1, C” and C-terminal of G are absent. The cysteine residues at 48 and 116 form intrachain disulfide bonds are drawn as balls and sticks, and are shown in gray (pink arrow for chPD-1 and yellow arrow for mouse PD-1). (F–H) Overlay of Ig V and Ig C domains of chPD-L1 with human PD-L1. (F) The Ig V and Ig C domains of chPD-L1 is shown in yellow, and the (G) Ig V and Ig C domains of human PD-L1 is shown in red. In human PD-L1, the two β-sheets are labeled AGFCC'C” and BED. In chPD-L1, A, C', and C” are absent. The cysteine residues at 43 and 120 of Ig V domain and at 133 and 225 of Ig C domain form intrachain disulfide bonds are drawn as balls and sticks, and are shown in blue (pink arrow for chPD-L1 and yellow arrow for human PD-L1). Both chPD-1 and chPD-L1 were showed in same view, respectively.