Figure 2.
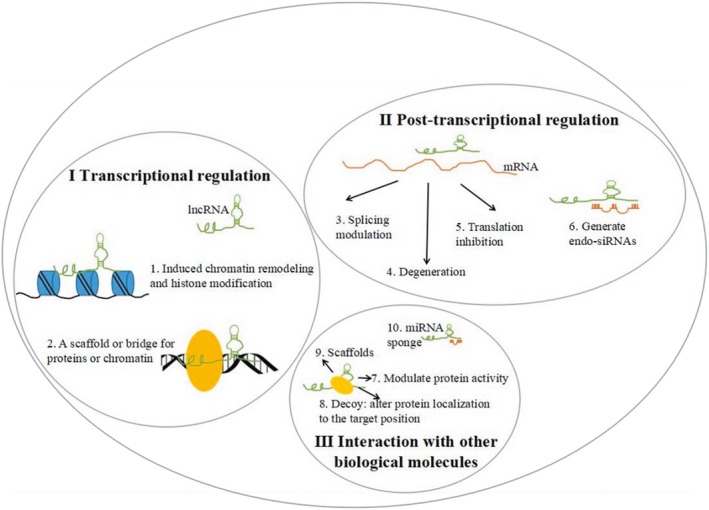
Functions of lncRNAs. I) Transcriptional regulation: lncRNAs can (1) induce chromatin remodeling and modification, and (2) act as a scaffold or bridge for proteins or chromatin. II) Post‐transcriptional regulation: lncRNAs can be combined with mRNA by base complementary pairs, to block the splice sites of the spliceosome, resulting in (3) alternatively spliced transcripts, (4) mRNA degeneration, (5) translation inhibition, or (6) the generation of endo‐siRNAs. III) Interaction with other biological molecules: lncRNAs can (7) bind to the specific protein partners to modulate protein activity, (8) act as a decoy to alter protein localization, (9) serve as scaffolds to allow the formation of larger RNA–protein complexes, or (10) interact with miRNA as a miRNA sponge
