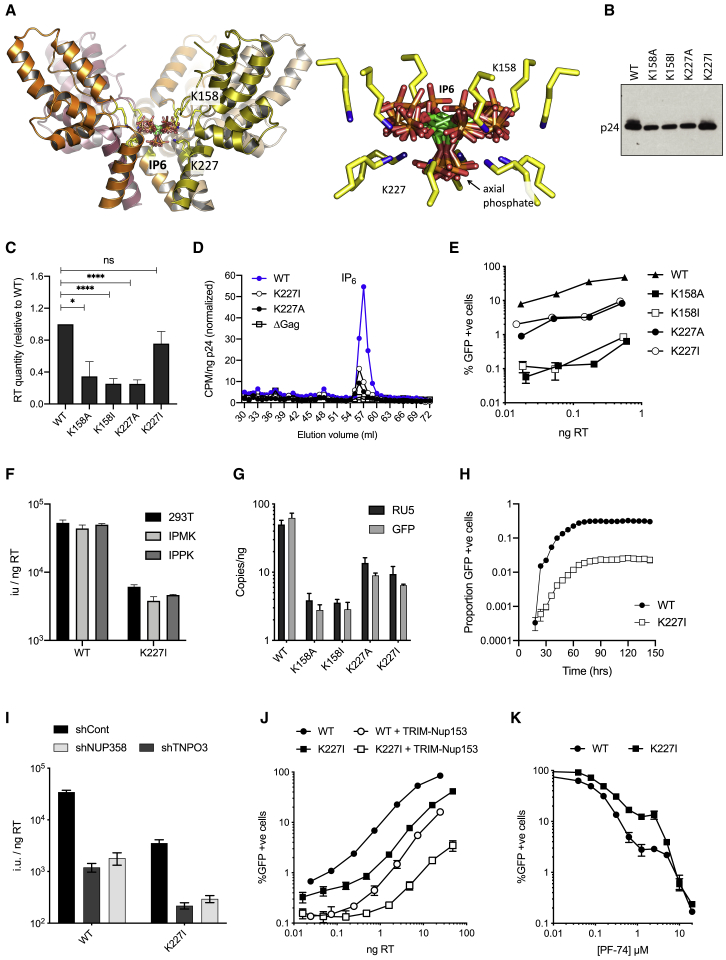
Figure 5.
Mutation of K158 and K227 Rings in Immature Gag Hexamers Affects Viral Production and Infectivity
(A) View of five subunits of the immature hexamer (on the basis of PDB: 6BHR) showing the lysine side-chains responsible for coordinating IP6 (blue sphere denotes the ε-amino group). Symmetrically equivalent molecules of IP6 are shown with the carbon rings in green.
(B) Western blot of pelleted virions to show p24 levels in HIV wild-type and mutant virions.
(C) Quantification of mutant virus production 293T cells as determined by RT levels in viral supernatants. Error bars depict mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Values are expressed as fold change from levels of RT produced in WT virus. The reduction in virus production between WT and K158A, K158I, and K227A is statistically significant (p = 0.0121, p < 0.0001, and p < 0.0001, respectively).
(D) Quantification of IP6 packaging in mutants K227A and K227I after normalization for background and input virus (per nanogram p24). Both K227 mutants package similarly reduced levels of IP6 with respect to wild-type virus. Representative data from two independent experiments are shown.
(E) Infectivity of lysine mutant viruses normalized to nanogram RT input. Each mutant pair gives similarly reduced levels of infection, with K158A/I largely impaired. Error bars depict mean ± SD of three replicates from one experiment representative of three independent experiments.
(F) Infectious titer of WT and K227I mutant viruses produced in WT 293T, IPMK-KO, and IPPK-KO cells. Infectivity is expressed as infection units (IU) per quantity of input virus (nanogram RT).
(G) Levels of reverse transcription products strong-stop (RU5) and post-strand-transfer (GFP) 4 h post-infection. Error bars depict mean ± SD of three replicates from one experiment representative of three independent experiments.
(H) Infectivity of WT and K227I virus matched for RT input over 150 h to determine whether K227I could recover infectivity over time. Infectivity is measured using an IncuCyte and determined as proportion of cell area that is GFP positive.
(I) HeLa cells stably expressing shRNA control or shNUP358 or shTNPO3 were infected with wild-type or K227I virus. Infection is quantified as infection units (IU) per quantity of input virus (nanogram RT).
(J) WT or TRIM-Nup153 expressing HeLa cells were infected with wild-type or K227I virus. The percentage infected cells was determined by percentage GFP positive cells for a range of input virus (quantified by nanogram RT).
(K) HeLa cells were infected with wild-type or K227I virus in the presence of anti-capsid inhibitor PF-74. Data are normalized to infection in the absence of inhibitor. Error bars depict mean ± SD of three replicates from one experiment representative of at least two independent experiments.