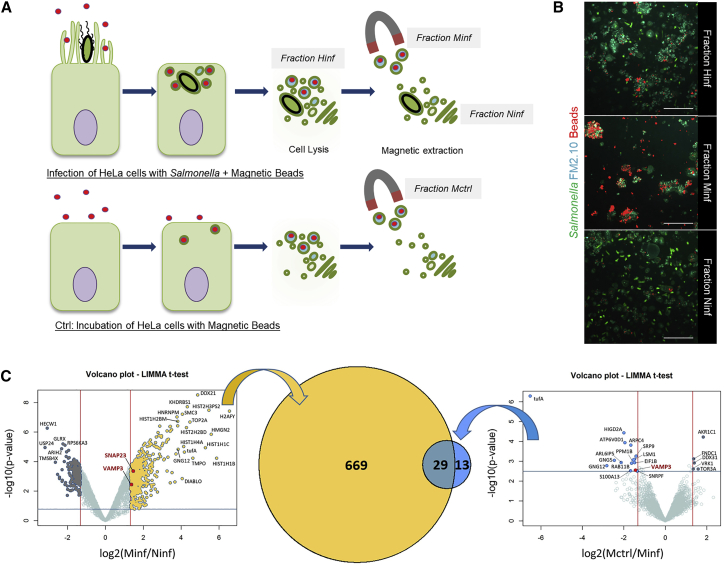
Figure 3.
Magnetic Isolation and Proteomic Analysis of IAMs
(A) Scheme of the IAM extraction (top panel) and the negative control (bottom panel).
(B) Fixed microscopy of the different fractions extracted and labeled with the membrane dye FM2-10 (in cyan). The bacteria are in green, and the magnetic beads are in red. Scale bars: 5 μm.
(C) Volcano plots of the proteomics results showing the respective enrichment in proteins in the Minf fraction compared to the Ninf fraction (yellow) and the Mctrl fraction (blue). Vertical lines correspond to minimal fold-changes of 2.5 between fractions and horizontal lines to a threshold on the p values associated with a false discovery rate (FDR) of 1%. Proteins detected in only one of the two compared fractions are not present on the Volcano plots. For complete protein lists, see Tables S1 and S2. The Venn diagram in the middle represents the numbers of proteins not related to DNA/RNA, nucleus, mitochondria, or ribosome. The yellow part corresponds to the proteins found more abundant in the Minf faction when compared to the Ninf fraction. The blue part corresponds to the proteins found more abundant in the Minf fraction when compared to the Mctrl fraction. 29 of these proteins are common to both comparisons.