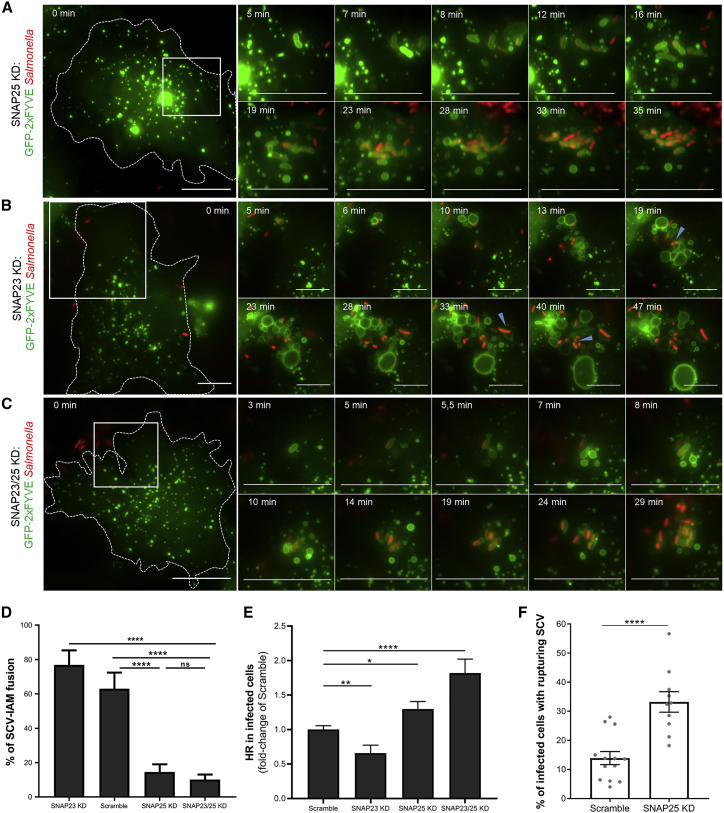
Figure 5.
Involvement of SNAP Proteins during SCV-IAMs Fusion Determining Salmonella Niches
(A–C) Time-lapse microscopy of IAM and SCV formations and interactions in HeLa cells transfected with GFP-2xFYVE (in green) and with a siRNA pool against SNAP25 (A), SNAP23 (B), or both (C). Cells were infected with fluorescent Salmonella (in red). Scale bars: 10 μm. Blue arrowheads designate fusion events. See Video S3A for (A); Video S3B for (B); Video S3C for (C); and Figure S3 for knockdown efficiencies.
(D) Quantification of the percentage of SCVs fusing with IAM upon knockdown of SNAP23, SNAP25, or both. Data were obtained from three independent experiments. p values were obtained after t test. Error bars: ±SEM.
(E) Quantification by high-throughput microscopy of the infected cells containing hyper-replicating salmonellae in HeLa cells transfected with an siRNA pool against SNAP23, SNAP25, or both. The graph represents data from three independent experiments that are normalized with respective values of the scramble. p values were obtained after t test. Error bars: ±SEM.
(F) Quantifications of the percentage of infected cells containing rupturing SCVs in HeLa cells transfected with an siRNA pool against SNAP25 or scrambled siRNA. Rupturing SCVs were quantified by time-lapse microscopy using the rupture reporter GFP-galectin-3. Acquisitions were performed at 20× every 2 min for 1 h pi. Each field was scored for its percentage of infected cells containing at least one rupturing SCV. Data were obtained from three independent experiments. p values were obtained after t test. Error-bars: ±SEM. See Figure S4 for method details and Video S4E.