Figure 8.
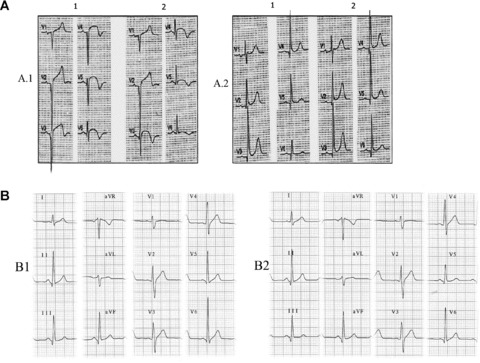
(A) Patient with acute myocardial infarction at subacute stage with V1–V6 Q waves and correctly placed precordial leads (A.1). Small changes of leftward misplacement of V3–V6 electrodes (A.2) cause significantly modified QRS morphology with qR in V6. According to classical nomenclature, the first ECG (A.1.1) would be interpreted as necrosis spreading to low lateral wall, and the second ECG (A.1.2) as no recorded spreading. A.2: Patient with inferolateral infarction (R ≥ S1 in V1) and QR in V6 (A2.1). After slight rightward displacement of the precordial leads, the QR pattern in V6 disappears. B.1: ECG of a healthy 45‐year‐old man with V6 > V5 voltage, which obliges us to review the placement of these two electrodes. B.2: Interchange between the two black colored electrodes, V5 and the ground lead (IEC), which imitates interchange between V6 and V5. In this case, we can observe the loss of S in V5 that is present in V4 and V6.
