Figure 4.
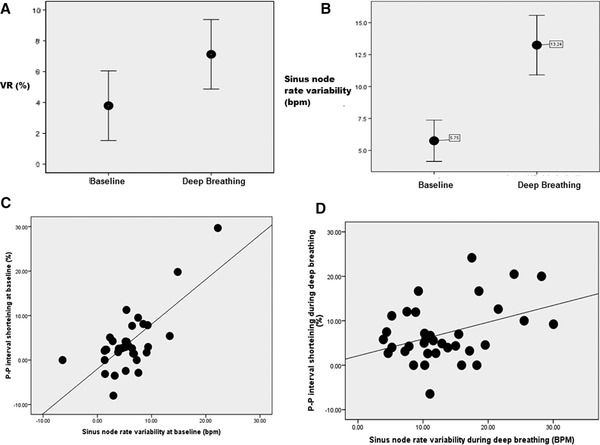
The relationship between P‐P interval shortening surrounding QRS complexes during heart block and sinus rate variability: (A). The magnitude of P‐P interval shortening during deep breathing (mean 7.1 ± 6.6%) was significantly greater than the P‐P interval shortening at baseline (mean 3.8 ± 6.6%, P = 0.009). (B) The sinus rate variability was also significantly greater during deep breathing (mean 13.3 ± 6.8 bpm) than at baseline (5.8 ± 4.7 bpm, P < 0.001). (C) At baseline, P‐P shortening positively correlated with the sinus rate variability (r = 0.47, P = 0.004). (D) During deep breathing, the magnitude of P‐P interval shortening also positively correlated with the amount of sinus rate variability (r = 0.39, P = 0.02).
