Figure 2.
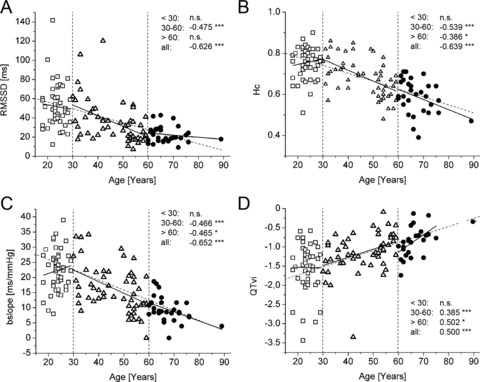
Correlations between cardiovascular autonomic parameters and age. (A) Root mean squared differences of successive normal‐to‐normal intervals (RMSSD). (B) Compression entropy, a complexity measure of heart rate time series, decreases similarly to RMSSD, but with higher correlation coefficients. (C) Decrease of baroreflex sensitivity with age as represented by bradycardic slopes (bslope). (A)–(C) are measures of vagal modulation of heart rate time series, which thus decrease in older age. (D) QT variability index, a measure of sympathetic influence at the level of the heart, increases with age, with an even enhanced steepness in the >60 years group. Correlation data are presented as r‐values and as linear fit regression lines for each age group separately (bold black lines) and for all age groups taken together (thin intermittent line). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; n.s. – not significant.
