Figure 2.
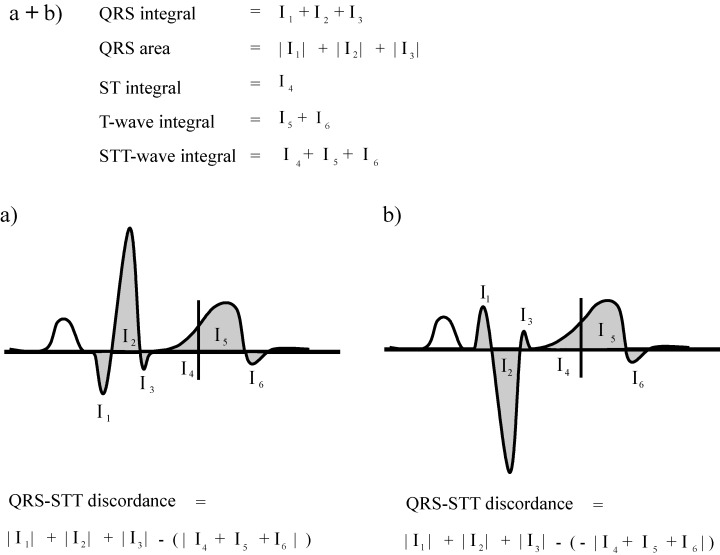
(a + b) Illustration of the calculation of QRS, ST‐segment, T wave, and ST‐T wave integrals, and QRS‐ST‐T discordance in each MCG channel. QRS integral was calculated as the time integral from the QRS onset to QRS offset. QRS area was calculated as the sum of absolute values of Q, R, and S wave areas. The ST‐segment, T wave, and ST‐T wave integrals were obtained as the corresponding time integrals. (a) If the main QRS deflection and the ST‐T wave were of same polarity, the ST‐T wave integral was subtracted from the QRS area when calculating the QRS‐ST‐T discordance. The QRS‐ST discordance and QRS‐T discordance were calculated in an analogous manner. (b) If the main QRS deflection and the ST‐T wave were of opposite polarity, the latter was multiplied by −1 when calculating the QRS‐ST‐T discordance. The QRS‐ST discordance and QRS‐T discordance were calculated in an analogous manner.
