FIGURE 2.
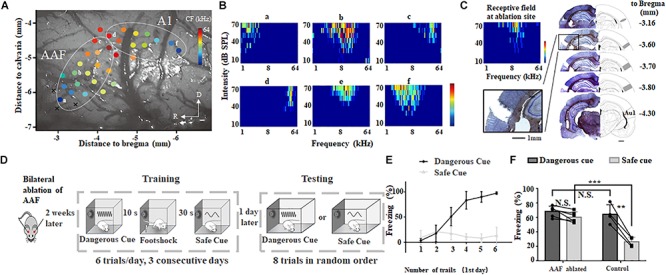
Bilateral ablation of AAF impairs animal’s categorization of dangerous and safe cue. (A) A representative tonotopic map in the left auditory cortex. Color dot shows the characteristic frequency (CF) at recording site. A1, primary auditory cortex; AAF, anterior auditory field; R, rostral; D, dorsal. (B) Six tonal receptive fields shown in A. (C) Ablation sites in auditory cortex. Images are modified from “The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates (6th Edition).” Scale bar, 1 mm. (D) Schematic drawing of training and testing protocol. (E) Freezing duration to sound cues during training session in the first day. (F) Comparison of freezing duration between AAF ablated rats (AAF ablated) and normal rats (control). ∗∗p < 0.01, paired t-test; ∗∗∗p < 0.001, t-test.
