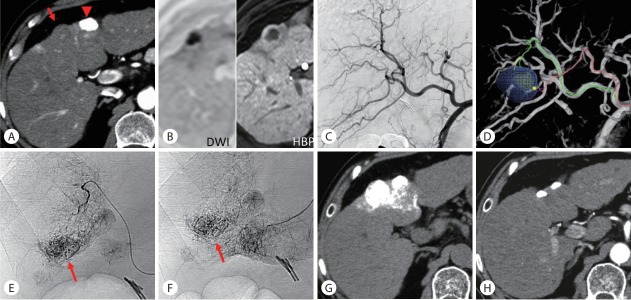
Figure 3.
Ultraselective conventional transarterial chemoembolization (cTACE) for hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma. (A) Arterial phase computed tomography (CT) showed a hypovascular tumor in segment 4 (arrow) near the previously embolized tumor (arrowhead). (B) The tumor showed hyperintensity on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and hypointensity with a hyperintense rim on hepatobiliary-phase of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI. (C) Common hepatic arteriogram showed no tumor staining. (D) TACE guidance software identified two tumor-feeders. (E, F) Each branch was selectively embolized using a 1.5-F tip microcatheter. The arrows indicate the tumor. (G) Unenhanced CT performed 1 week after ultraselective cTACE showed iodized oil accumulation in the entire tumor. (H) Arterial phase CT performed 1 year and 2 months after ultraselective cTACE showed complete tumor necrosis. DWI, diffusion-weighted image; HBP, hepatobiliary-phase.