Figure 6.
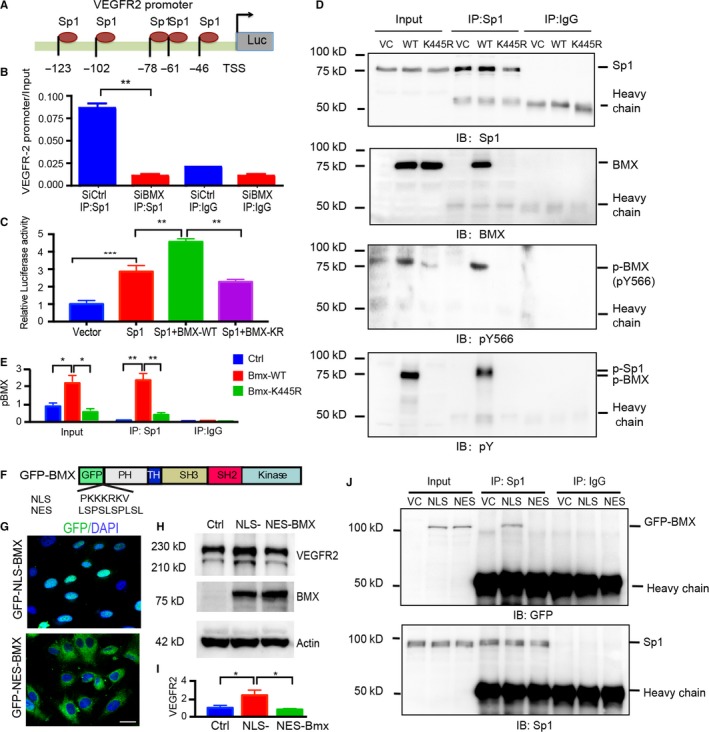
Active BMX interacts with Sp1 in the nucleus and facilitates Sp1 binding to the Vegfr2 promoter. A, Schematic diagram for the Sp1 binding sites located on the Vegfr2 promoter. −123 to −46 are positions related to the transcription start site (TSS; +1). B, BMX promotes Sp1 binding to the Vegfr2 promoter. HDLECs were transfected with human BMX siRNA or control siRNA (20 nmol/L) for 48 h. ChIP assay was then performed with Sp1 antibody. An Sp1 binding region of the Vegfr2 promoter was used as a primer for quantitative PCR. C, HUVECs were cotransfected with a Vegfr2 reporter (−123 to +1), Renilla luciferase plasmid and either vector control (Vector), BMX‐WT or kinase‐dead K445R‐BMX alone or together with Sp1 for 48 h. The dual‐luciferase assay was then performed. The firefly luciferase readout was normalized to that of Renilla luciferase. The data are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. **, P < .01; ***, P < .0001. D‐E, HUVECs were infected by BMX‐WT or BMX‐K445R lentivirus. The nuclear fractions were isolated, and the association of BMX with Sp1 was determined by immunoprecipitation with anti‐Sp1 antibody, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti‐Sp1, anti‐BMX, anti‐BMXpY566 and anti‐phosphor‐tyrosine (anti‐pY). IgG was used to a control. Quantification of p‐BMX was presented in (E). F‐G, Location of NLS‐BMX and NES‐BMX. F, Schematic diagram of GFP‐NLS‐BMX and GFP‐NES‐BMX. Insertion of a NLS (PKKKRKV) or NES (LSPSLSPLSL) is indicated. G, HUVECs were infected by lentivirus expressing GFP‐NLS‐BMX or GFP‐NES‐BMX, and location of BMX was visualized under fluorescence microscope. H‐J, NLS‐BMX, but not NES‐BMX, increases VEGFR2 and binds to Sp1. HUVECs were infected by lentivirus expressing vector control, GFP‐NLS‐BMX or GFP‐NES‐BMX. VEGFR2 expression was determined by Western blotting (H) with quantification in (I), and association of BMX with Sp1 was determined by co‐immunoprecipitation (J)
