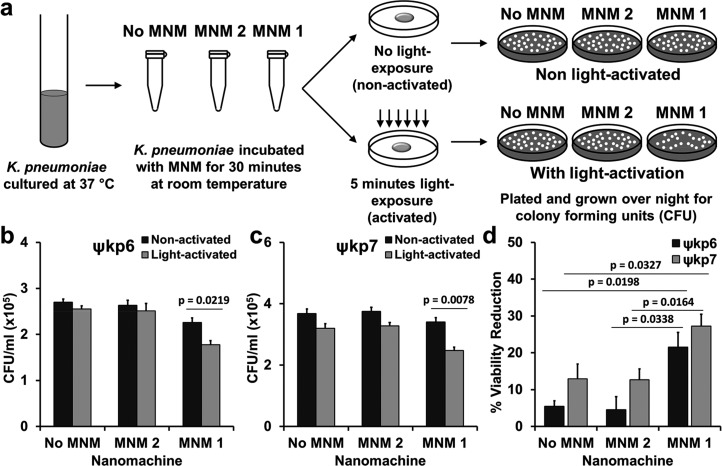
Figure 3.
Viability reduction of K. pneumoniae with light-activated molecular nanomachines. (a) Experimental setup for bacterial viability reduction assays. A log growth phase culture of K. pneumoniae incubated with no MNM (dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)), MNM 2, or MNM 1 for 30 min, activated with 365 nm light for 5 min and plated for CFU/mL counts. (b) Extensively drug-resistant strain of K. pneumoniae (ψkp6, AR-0666) exposed to no MNM (DMSO), 10 μM of MNM 2, or 10 μM of MNM 1. Comparison of CFU/mL of K. pneumoniae after MNM exposure, without and with light activation. (c) Antibiotic-sensitive strain of K. pneumoniae (ψkp7, NIH-1) exposed to no MNM (DMSO), 10 μM of MNM 2, or 10 μM of MNM 1. Comparison of CFU/mL of K. pneumoniae after MNM exposure, without and with light activation. Results presented are means and standard error from four replicates for each group. The p values are from an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test.