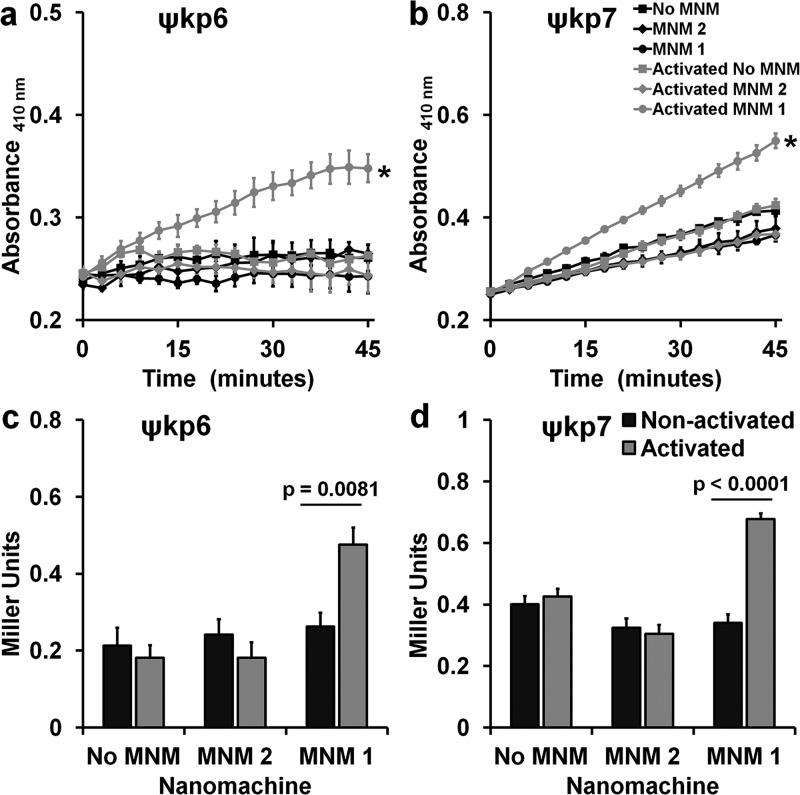
Figure 4.
Cell wall inner membrane permeability with and without light activation of molecular nanomachines. Cell wall inner membrane permeability of K. pneumoniae exposed to no MNM (DMSO), 10 μM of MNM 2, or 10 μM of MNM 1 determined by cytoplasmic β-galactosidase activity using o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactoside (ONPG) as the substrate, measured with an increase in absorbance at 410 nm. (a,c) Extensively drug-resistant strain of K. pneumoniae (ψkp6, AR-0666) exposed to MNM. (a) Comparison in absorbance at 410 nm of K. pneumoniae with ONPG after MNM exposure, without (nonactivated) and with light activation (activated). (b,d) Antibiotic-sensitive strain of K. pneumoniae (ψkp7, NIH-1) exposed to MNMs. (b) Comparison in absorbance at 410 nm of K. pneumoniae with ONPG after MNM exposure, without (nonactivated) and with light activation (activated). (c,d) ONPG assay at 30 min with Miller calculation for inner membrane permeability of K. pneumoniae exposed to no MNM (DMSO control), 10 μM of MNM 2, or 10 μM of MNM 1. Comparison of inner membrane permeability of K. pneumoniae after MNM exposure, without and with light activation. Results presented are means and standard error from four replicates for each group. (a–c) Values of *p < 0.05 are from a one-way ANOVA. (c,d) Values of p are from an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test.