Table 4.
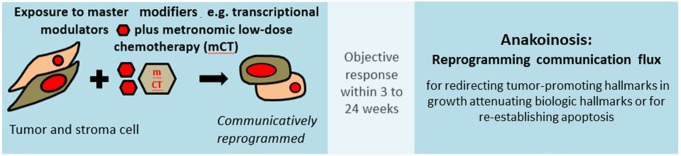
Diversification of non-curative care by re-establishing growth attenuating biologic hallmarks via pro-anakoinotic processes.
 | |
|---|---|
| Re-establishing growth attenuating biologic hallmarks or apoptosis | |
| Combinations of master modifiers: resetting tumor systems | References |
|
Biologic outcome: Changes in tumor biology • Simultaneous modeling of heterologous cell compartments and pathways • Tumor stem cell quiescence: Targeting the tumor cell niche • Simultaneous inflammation control, anti-angiogenesis, immunologic tumor control, modeling of tumor metabolism • Targeting dysregulated homeostatic pathways • Targeting tumor system's robustness • Induction of differentiation with regain of function, transdifferentiation, biologic memory • Therapy effects beyond therapy discontinuation: Induction of biologic memory • Attenuation of metastatic spread or outgrowth Clinical outcome: Interactions of cellular compartments, tumor-organ and -organism interactions • “Off-target” effect: Tumor cell death followed by continuous complete remission (alternative pro-apoptotic pathways) • Resolution of cachexia while stabalizing metastatic tumor disease • Favorable effects on efficacy of consecutive therapies (progression-free survival 2) • Pro-anakoinotic therapies replace temporary complete remission or molecular complete remission by long-term disease stabilization at minimized toxicity (replicative arrest or tumor dormancy) • Inhibition of further metastatic spread following progression after pro-anakoinotic therapy • Tumor control via resetting interaction of tumor harboring organ and tumor |
(8–11, 18, 33, 54, 58, 59, 94, 98–104) |
Master modifiers facilitate reprogramming of tumor tissue, for example via agonists of nuclear transcription factors, which exploit—from a communication technical view—the tumors' “background knowledge”.
