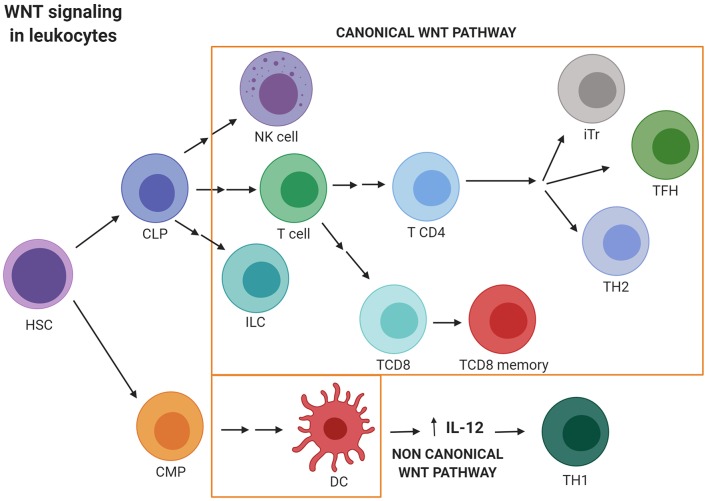
Figure 2.
WNT signaling activation in leukocytes. Canonical WNT signaling promotes T cell lymphopoiesis and regulates peripheral T cell activation and differentiation. Thus, canonical WNT activity promotes differentiation into the TH2 and TFH subsets. Regulatory T (Tr) cells survival is also promoted by the canonical WNT pathway. Nevertheless, TCF1 limits the suppressive activity exerted by Tr in the effector T cell population. Finally, WNT/β-catenin activation is essential for the development of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) natural killer (NK) cells and DC differentiation. Conversely, non-canonical WNT signaling induces the secretion of IL-12 by dendritic cells favoring TH1 responses. CLP, Common lymphoid progenitor; CMP, Common myeloid progenitor; DC, Dendritic cell; ILC, Innate lymphoid cell; iTr, induced regulatory T cell; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; NK, Natural killer; TFH, T follicular helper cell; TH, T helper. Created with BioRender.com.