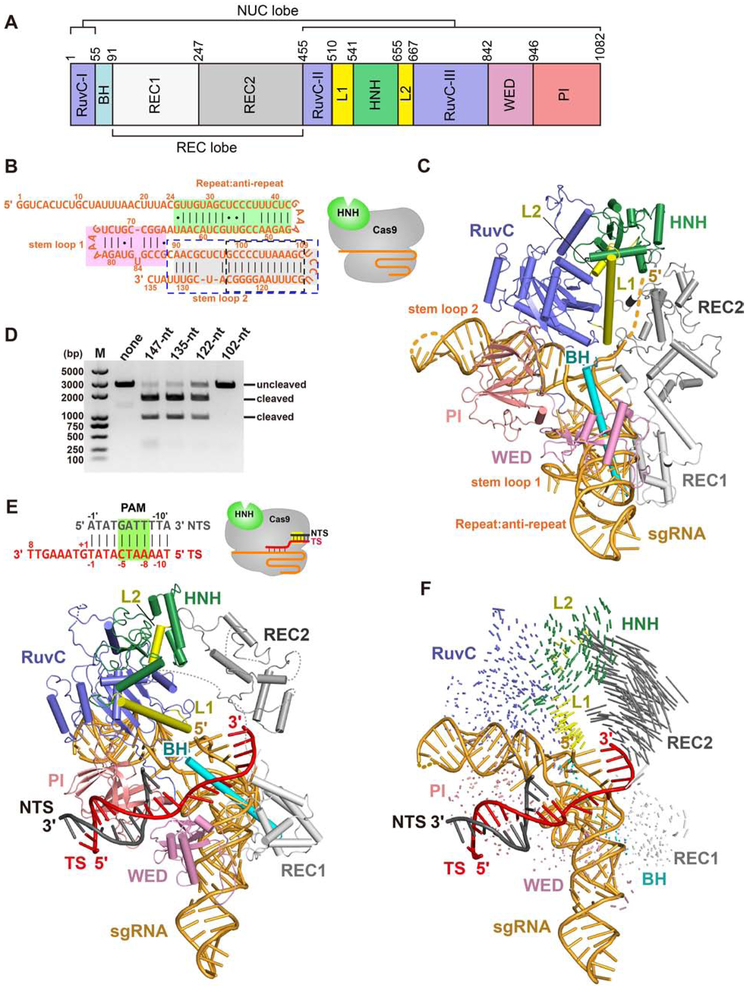
Figure 1. The overall structure of Nme1Cas9 in complex with truncated sgRNA.
A. Domain organization of Nme1Cas9.
B. Schematic representation of the 135-nt sgRNA used for crystallization. The repeat:anti-repeat region is highlighted in green background. The stem-loops 1 and 2 are highlighted in pink and grey background, respectively. The black and blue dashed-line boxes indicate the truncated nts of the 122-nt and 102-nt sgRNAs, respectively. The cartoon diagram represents the state of Nme1Cas9 in this structure.
C. Crystal structure of the Nme1Cas9-sgRNA binary complex. Individual Nme1Cas9 domains are colored according to the scheme in Figure 1A.
D. DNA cleavage by wild-type and mutant Nme1Cas9 using linearized plasmid DNA containing a target sequence fully complementary to the sgRNA, and various sgRNAs containing different truncations.
E. Top: schematic representation of the partially double-stranded DNA target with its TS complementary to guide nts 17-24 (seed only). Bottom: crystal structure of the seed-only Nme1Cas9-sgRNA-dsDNA complex.
F. Conformational changes of Nme1Cas9 before (C) and after (E) PAM recognition and seed pairing.
See also Figures S1, S2, and Table S1.