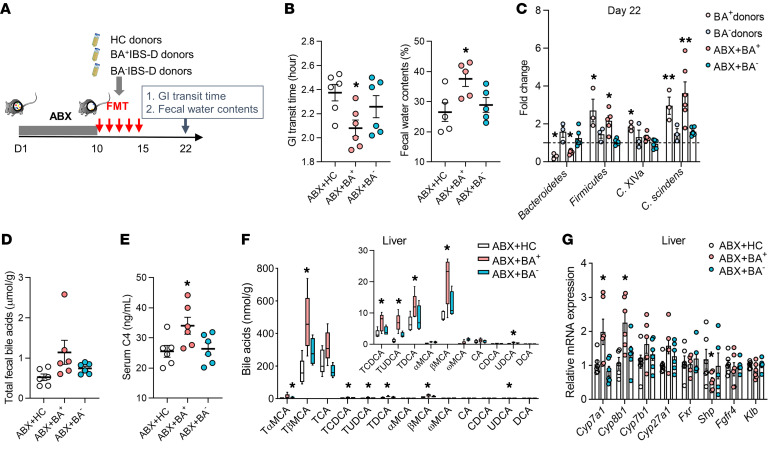
Figure 3. Excessive BA synthesis and excretion in mouse recipients receiving BA+IBS-D fecal microbiota.
(A) Experimental procedure for fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) in antibiotic cocktail–induced (ABX-induced) pseudo-germ-free mice (n = 6/group). Mice that received fecal microbiota of HC donors were grouped as ABX+HC, and mice treated with fecal microbiota from BA+IBS-D and BA–IBS-D donors were classified as ABX+BA+ and ABX+BA–, respectively. (B) The GI transit time and fecal water contents of mouse recipients. (C) Relative levels of BA-related bacteria in feces of donors and mouse recipients based on qPCR analysis. (D and E) The levels of total fecal BAs and serum C4 in mouse recipients. (F) Hepatic BA profiles of mouse recipients. (G) Relative gene expression of BA synthetic regulators in the hepatic tissues of mouse recipients. Differential BA-related phenotypes, bacteria, and genes are shown as mean ± SEM. BA metabolites are expressed with 5th–95th percentile values. Differences were assessed with the Kruskal-Wallis test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the ABX+HC group. Cyp7a1, Cyp8b1, Cyp7b1, Cyp27a1, Fxr, Shp, Fgfr4, and Klb represent the mRNAs for the proteins cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase, sterol 12α-hydroxylase, steroid 7α-hydroxylase, sterol 27-hydroxylase, farnesoid X receptor, small heterodimer partner, fibroblast growth factor receptor 4, and Klothoβ, respectively.