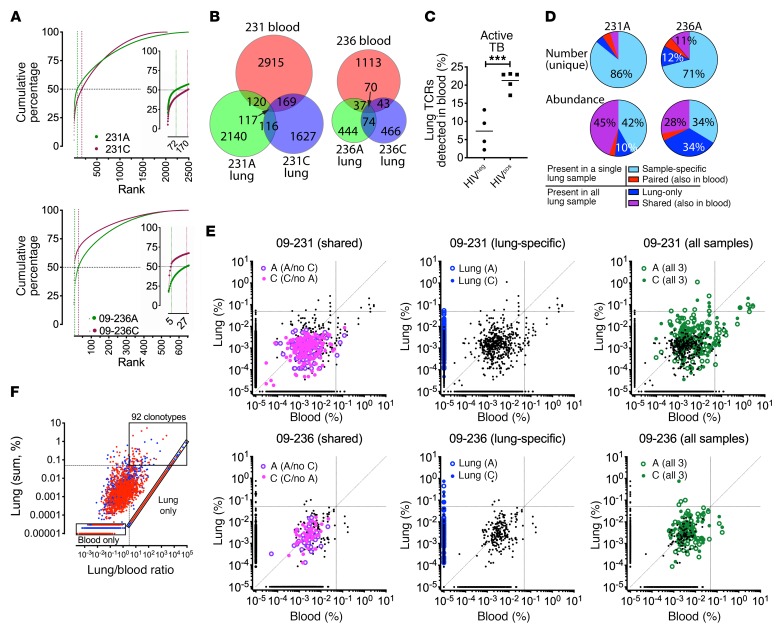
Figure 7. TCRδ clonotypes detected in TB lung granulomas.
(A) Cumulative frequency of lung TCRδ clonotypes from 2 representative HIVneg subjects with active TB (09-231 and 09-236). Vertical dotted lines indicate the number of clonotypes comprising 50% of the total lung TCRδs. (B) Overlap of TCRδ clonotypes detected in the blood and lung tissue of subjects 09-231 and 09-236. (C) Percentage of lung TCRδ clonotypes detected in the blood (i.e., common to blood and lung) for subjects with active TB. (D) Number of TCRδ clonotypes unique to lung samples from subjects 09-231A and 09-236A, shared with blood only, shared with other lung samples, or detected in all 3 samples (top pie charts). Relative abundance of the TCRδ clonotypes in these groups (bottom pie charts). (E) Groups of TCRδ clonotypes differed in their abundance. Lung frequency of each TCRδ clonotype versus its blood frequency. For clonotypes not detected, the frequency was assigned 0.00000011. All unique clonotypes are shown in black. Specific groups of clonotypes are shown in color as follows: paired (shared between 1 lung sample and blood; purple); lung-specific (blue); or shared (in all 3 samples; green). Open circles indicate the frequency in lung type A lesions; solid circles indicate the frequency in lung type B lesions. Horizontal and vertical lines equal 0.05%. Diagonal is the line of equivalency. (F) Identification of abundant and lung-enriched TCRδ clonotypes. For each of 32,000 unique clonotypes from 9 subjects, the sum of the frequencies in lung versus the lung/PBMC ratio for each clonotype was plotted. For clonotypes not detected, the frequency was assigned 0.00000011. Abundant and enriched clonotypes were defined as having a sum frequency of greater than 0.05% (horizontal dotted line) and a lung/PBMC ratio of greater than 3 (vertical dotted line). Blue represents HIVneg; red represents HIVpos. Bottom left and diagonal boxes indicate clonotypes detected only in blood or lung, and top right box indicates 92 abundant and enriched clonotypes. ***P < 0.001, by Student’s t test. Error bars indicate the median.