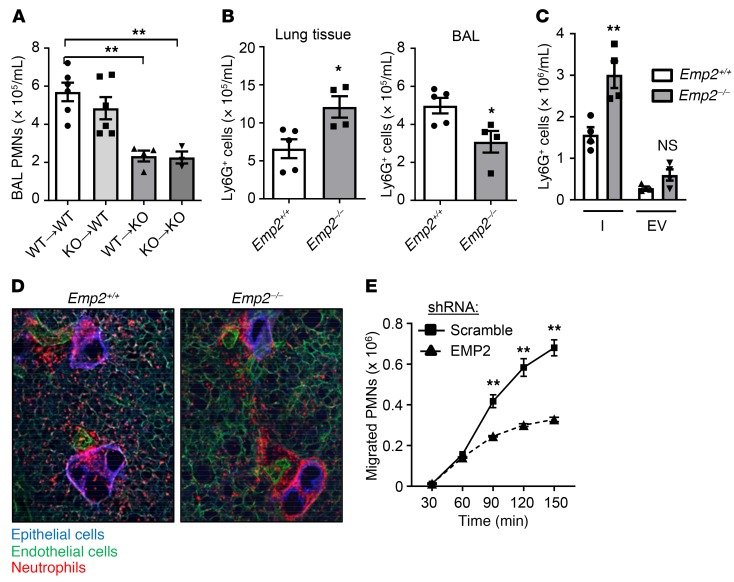
Figure 2. EMP2 regulates transepithelial migration of neutrophils into the alveolar lumen.
(A) Bone marrow chimeric mice were made by transfer of bone marrow cells from Emp2+/+ (WT) or Emp2–/– (KO) donors to Emp2+/+ or Emp2–/– irradiated recipients (donor[arrow]recipient). Chimeras were exposed to inhaled LPS, and BAL PMNs quantified 24 hours later (n = 3–6/chimera). (B) Eight hours after LPS inhalation, Ly6G+ PMNs were quantified by flow cytometry in lavaged and perfused lungs (left) and in the BAL (right) of Emp2+/+ and Emp2–/– mice (n = 4–5/genotype). (C) Pulmonary interstitial (I) and endovascular (EV) Ly6G+ PMNs were quantified under similar conditions to those in panel I (n = 4/genotype). (D) Live lung slices from Emp2+/+ and Emp2–/– mice were stained for E-cadherin (epithelium), CD31 (endothelium), and Ly-6G (PMNs) 6 hours after LPS. Emp2–/– lungs display an excess accumulation of peribronchovascular (interstitial) PMNs. Results are representative of n = 3–4/genotype. (E) Human PMNs that transmigrated across a monolayer of scramble or EMP2 shRNA-transduced Calu-3 cells in response to fMLP during a time course were quantified (n = 3/condition/time point). Data are the mean ± SEM and are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 analyzed using ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test in A, or unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test in B, C, and E.