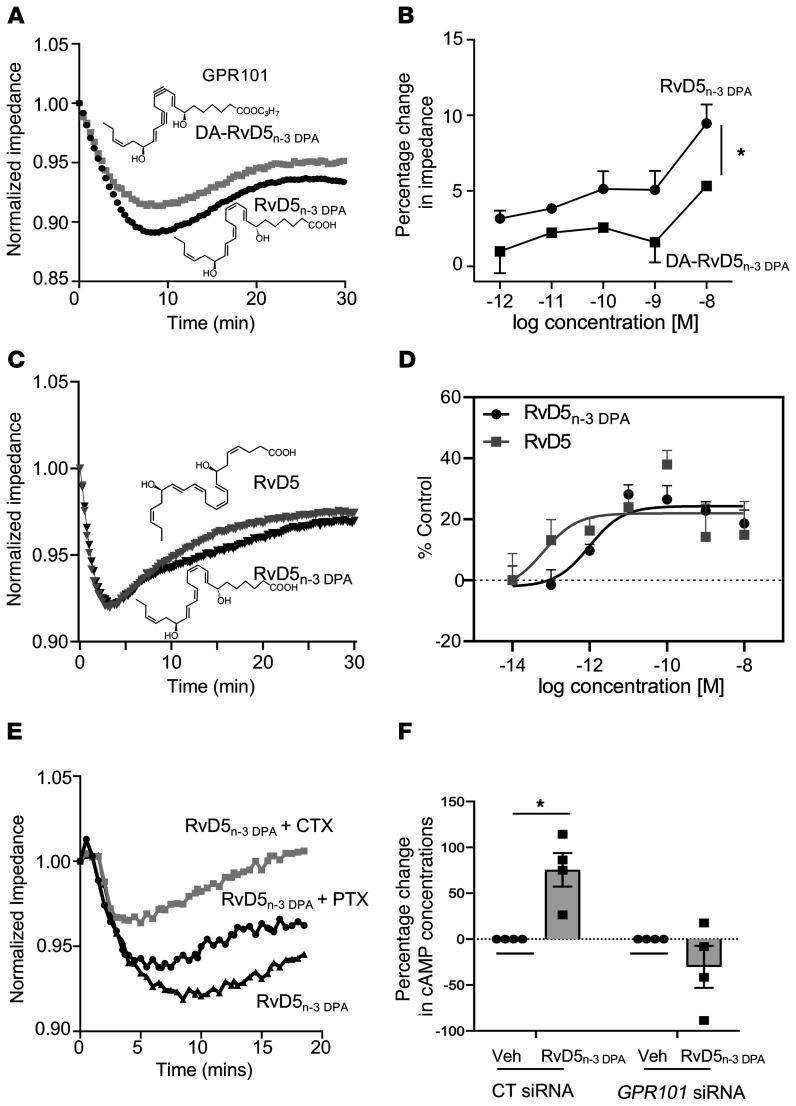
Figure 3. RvD5n-3 DPA stereospecifically activates GPR101 and increases cAMP in human macrophages.
(A) GPR101-expressing CHO cells were incubated with RvD5n-3 DPA or DA-RvD5n-3 DPA (10 nM), and impedance was measured for 30 minutes. Results are representative of 3 distinct experiments. (B) GPR101-expressing CHO cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of the ligands described in A, and changes in impedance from baseline values were determined at t = 10 minutes. Results represent the mean ± SEM. n = 3 from 3 distinct experiments. *P < 0.05; 1-way ANOVA with a Holm-Sidak post hoc multiple comparisons test. (C) GPR101-overexpressing CHO cells were incubated with RvD5n-3 DPA or DHA-derived RvD5 (1 nM), and cell impedance was measured over a 30-minute period using the xCELLigence DP system. Results are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 4 in 3 independent experiments). (D) CHO cells expressing GPR101 coupled with the β-arrestin luminescence reporter system were incubated with the indicated concentrations of RvD5n-3 DPA, DHA-derived RvD5, or vehicle (cell-plating reagent containing 0.01% ethanol), and receptor activation was measured as an increase in luminescence signal. Results are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3 in 2 independent experiments). (E) GPR101-expressing CHO cells were incubated with CTX (1 μg/mL, 2 hours), PTX (1 μg/mL, 16 hours), or vehicle and then with RvD5n-3 DPA (10 nM), and impedance was measured over a 30-minute period. Results are representative of 3 distinct experiments. (F) Human monocyte–derived macrophages were incubated with either an siRNA against GPR101 or a control sequence (CT siRNA; 72 hours at 37°C) and then with RvD5n-3 DPA (10 nM) or vehicle (Veh) (PBS containing 0.01% ethanol) for 2 minutes, and cAMP concentrations were assessed. Results represent the mean ± SEM (n = 4 donors). *P < 0.05; 1-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak post hoc multiple comparisons test.