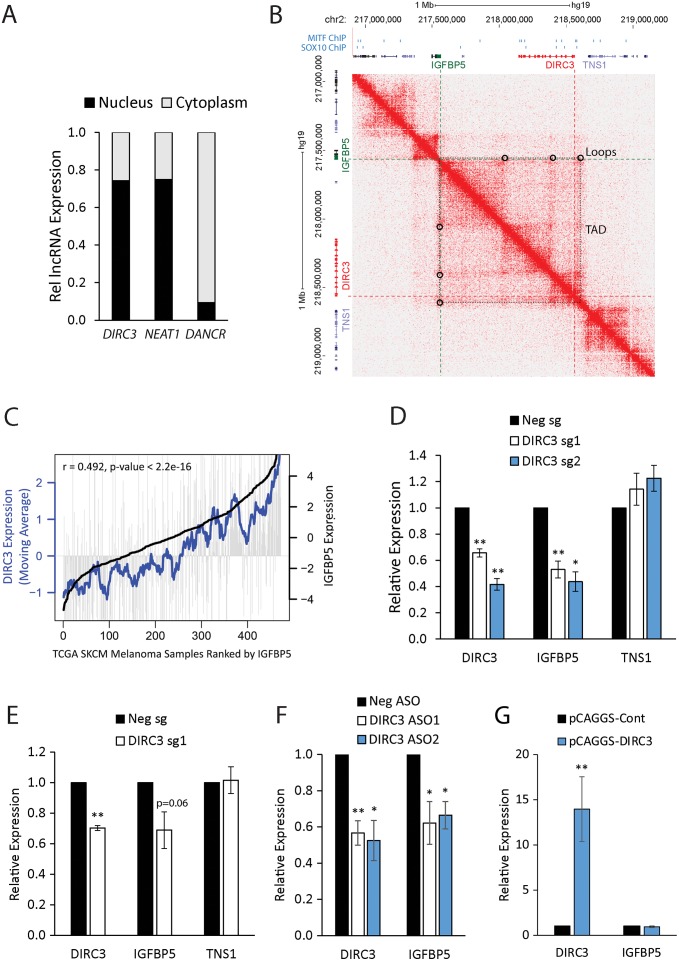
Fig 3. DIRC3 acts locally to activate expression of the adjacent IGFBP5 tumour suppressor gene.
(A) DIRC3 transcript is enriched in the nucleus in melanoma cells. SK-MEL-28 cells were biochemically separated into cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. The relative levels of DIRC3 and control DANCR (cytoplasm) and NEAT1 (nuclear) transcripts in each fraction were determined by qRT-PCR. (B) DIRC3 and IGFBP5 are located within the same TAD. Heatmap displaying chromosomal interactions, measured using HiC, at regions surrounding DIRC3 (red), IGFBP5 (green) and TSN1 (purple), shown in gene browser view, in NHEK (chr2: 217,000,000–219,000,000). The dotted black square box on the heatmap represents a TAD. Chromosomal looping interactions are indicated by black circles. MITF and SOX10 binding sites are denoted as blue boxes. (C) DIRC3 expression correlates with IGFBP5 in melanoma patient samples. Analysis of DIRC3 expression in TCGA human melanoma samples ranked by increasing IGFBP5. Vertical grey lines indicate DIRC3 expression in each melanoma sample. Bold black indicates IGFBP5 expression; the blue line is the moving average of DIRC3 expression across 20 melanoma samples. (D-F) DIRC3 specifically activates IGFBP5 expression in a transcript dependent manner. DIRC3 levels were depleted by dCas9-KRAB mediated CRISPRi (D), steric hindrance with dCas9 (E) or ASO LNA GapmeR mediated transcript degradation (F) in SK-MEL-28 cells. Expression of DIRC3 and the indicated neighbouring genes were measured using RT-qPCR with results normalised to POLII. Expression changes are shown relative to a non-targeting control (set at 1). (G) Ectopic DIRC3 fails to activate IGFBP5. SK-MEL-28 cells were transfected with pCAGGS-DIRC3 or pCAGGS alone and cells harvested for expression analysis 3 days later. Results are presented relative to the pCAGGS control. For all RT-qPCR reactions, mean values +/- SEM are shown, n≥3. One-tailed student’s t-test p < 0.05 * p < 0.01 **