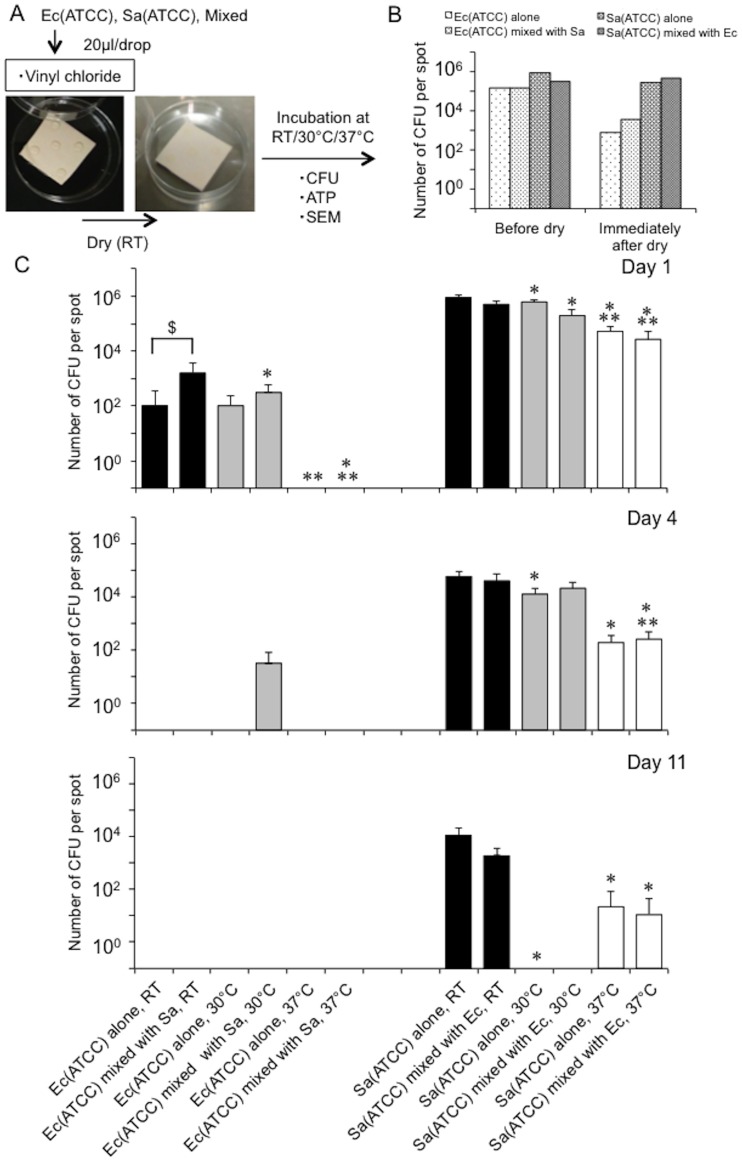
Fig 1. Representative human pathogenic bacteria favor lower temperatures for their survival on vinyl chloride surfaces.
A. Experimental protocol. Bacterial survival was monitored for mixed or single bacteria on vinyl chloride at distinct temperatures [RT (around 20°C), 30°C, 37°C] for 11 days by a CFU assay (CFU), ATP assessment (ATP) and morphological changes (SEM). Ec, E. coli (ATCC 25922). Sa, S. aureus (ATCC 29213). B. Bacterial numbers immediately (within 20 min) after drying. Ec, E. coli (ATCC 25922). Sa, S. aureus (ATCC 29213). C. Changes in bacterial numbers at distinct temperatures [RT (around 20°C), 30°C, 37°C] over 11 days, as determined by a CFU assay. Ec, E. coli (ATCC 25922). Sa, S. aureus (ATCC 29213). *, p<0.05 vs. the values at room temperature. **, p<0.05 vs. 30°C. †, p<0.05 between the bars.