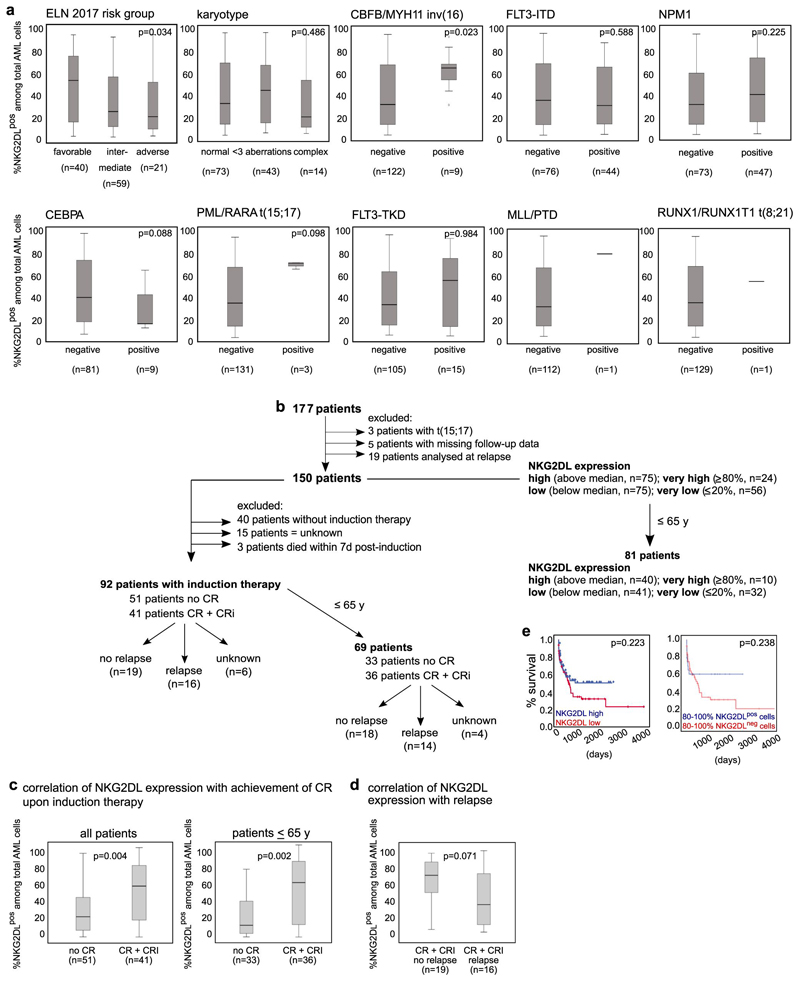
Extended Data Fig. 3. Association between surface expression of NKG2DLs and molecular and clinical parameters in patients with AML.
a, Cells from patients with known genetic and molecular profiles were stained with conjugated NKG2D–Fc chimeric protein and included in the analyses. Numbers of patients with positive or negative results for the respective mutation are shown below each analysis; patients with an unknown result for the particular analysis are not shown. Note that cases of AML that belong to the favourable molecular European LeukaemiaNet (ELN) risk group or with detectable inv(16) showed higher expression of NKG2DLs when compared to AML of other risk groups or without inv(16). For statistical analyses, a Kruskal–Wallis test was used for karyotype and ELN 2017 risk group, and a Mann–Whitney U test for all other data. b–e, Surface expression of NKG2DLs assessed at diagnosis (b) was compared between patients who achieved or did not achieve complete remission (CR) or complete remission with incomplete haematologic recovery (CRi) after induction chemotherapy (c), as well as between those patients who—after achieving complete remission (both with and without incomplete haematologic recovery)—did or did not experience subsequent relapse (d). Patients with initial high percentages of NKG2DL+ cells among total AML cells more often achieve—and, by trend, also sustain—remission. A Mann–Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis. a, c, d, Boxes indicate the median and interquartile range, and whiskers represent data up to 1.5 × the interquartile range; outliers that range from 1.5–3 × the interquartile range are depicted as circles. In e, patients with high (n = 75) versus low (n = 75) expression of NKG2DLs (left), and patients with ≥80% NKG2DL+ (n = 24) versus ≥ 80% NKG2DL−(n = 56) cells among total AML cells (right) were compared with respect to overall survival. Note that when only patients younger than 65 years are included, improved survival is observed in cases with ≥80% NKG2DL+ compared to ≥80% NKG2DL− cells among total AML cells (as shown in Fig. 1p). For survival analyses, the log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test was used for statistical analyses. For all other tests, two-sided statistical tests were used.