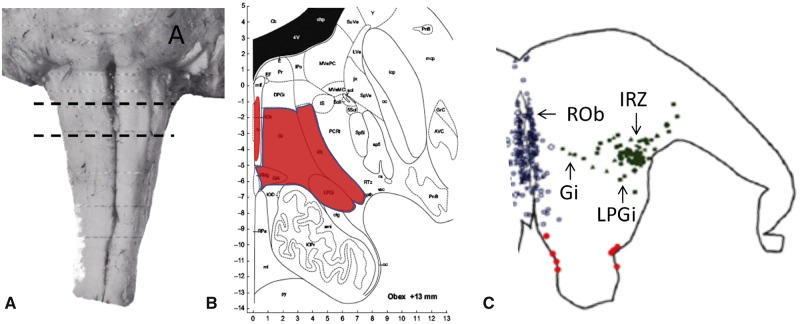
FIGURE 2.
(A) Location of the core lesion in SIDS in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata. (B) The nuclei that form the core lesion are paragigantocellularis lateralis (LPGi), the intermediate reticular zone (IRt), the gigantocellularis (Gi), the gigantocellularis pars alpha (GiA) (see text), raphe obscurus, (ROb), and arcuate nucleus (not shown). From the atlas of Paxinos et al (33) used with permission from Elsevier. (C) Computer-based plot of the topography of serotonergic neurons (as determined by the PH8 anybody) in a representative section of the rostral medulla in a postneonatal infant in the SIDS age range (37). Each circle represents a 5-HT neuron in the raphe midline (blue), extra raphe lateral to the midline (green), and ventral surface (red).