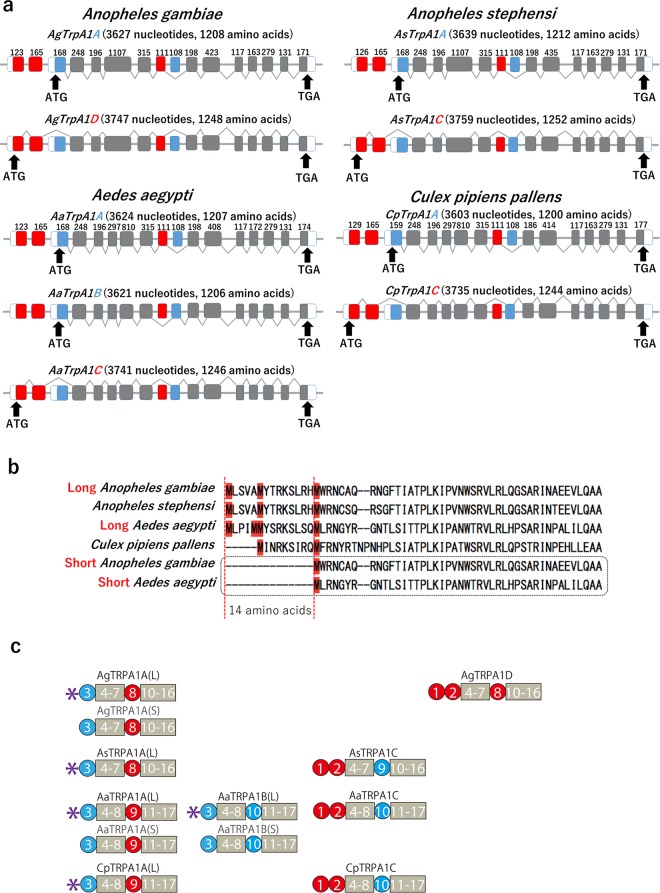
Figure 1.
Multiple isoforms of TRPA1 are expressed by Anopheles gambiae, Anopheles stephensi, Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens pallens. (a) Schematic mRNA structures of AgTrpA1A, AgTrpA1D, AsTrpA1A, AsTrpA1C, AaTrpA1A, AaTrpA1B, AaTrpA1C, CpTrpA1A and CpTrpA1C. Each rectangle represents an exon. Black arrows indicate the start point for translation. Exons in the same transcript are connected with grey broken lines. Blue and red boxes are alternatively spliced exons. (b) Amino acid sequence alignments of the N-terminus of AgTRPA1A, AaTRPA1A and AaTRPA1B. The black dot box indicates the previously reported short sequences of AgTRPA1A, AaTRPA1A and AaTRPA1B, which lose 14 amino acids (between 2 red dashed lines) compared with the long TRPA1B sequences. Methionine codons located in this region are highlighted in red. (c) A cartoon summarizes all the mosquito TRPA1 transcripts which are systematically compared in the following experiments. Transcripts with (S) have been reported. Purple asterisks indicate the peptides which were newly recognized in this study. Numbers in circles and boxes indicate the order of exons illustrated in (a).