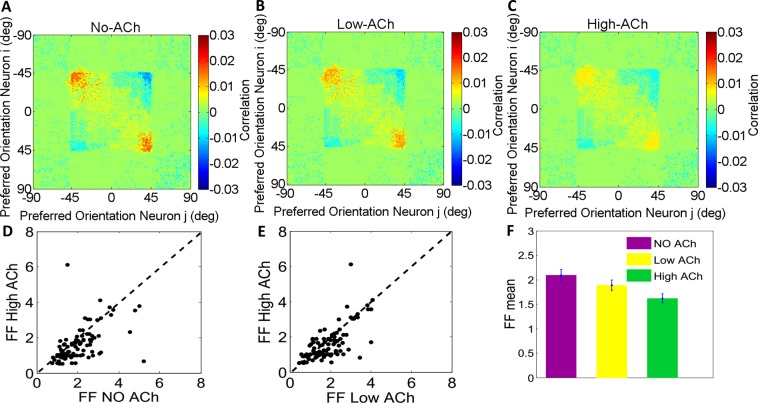
Figure 3.
Cholinergic Modulation Induces Conspicuous Decorrelation and Enhances Response Reliability. ACh significantly decreased noise correlations. Spike count noise correlation is plotted for the pair of neurons and compared to the NO-ACh condition. (A) both concentrations (low & high) of applying ACh are significantly reduced noise correlations (B & C) respectively. The principal diagonal was omitted for clarity. (D) Fano factor (FF) distribution for administration of ACh and No-ACh condition. Measured at a bin size of 100 ms counting intervals spaced over the duration of the trial (filled circles). (E) As in (D) but distribution for administration of high level versus low level of ACh. (F) Bar graphs show mean of the respective distributions and SEM. The variability was significantly reduced when ACh was applied in different concentration compared to the control condition; p values indicate whether ACh application significantly affected FFs (two-factor ANOVA, ACh applied vs. not applied).