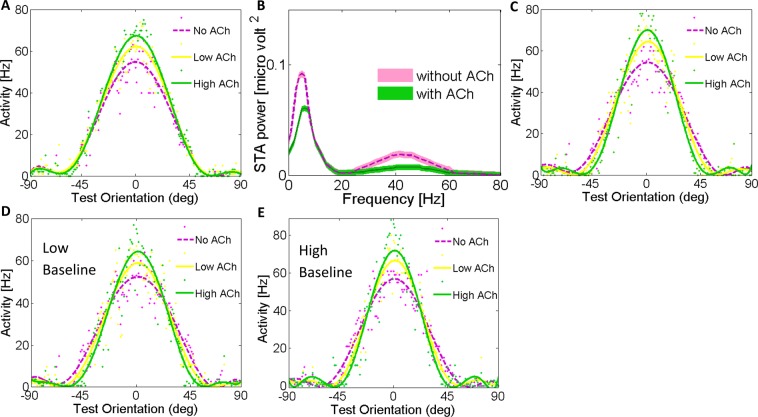
Figure 5.
Acetylcholine Causes a Scaling of Neuronal Tuning Curves through administration to excitatory neurons And Comparison of Cholinergic Modulation between Two Excitatory pools S1 and S2 on the STA LFP Power Spectra. (A) Effects of applying ACh on the tuning curves of the individual neurons through administration to excitatory neurons, leads to significant sharpening without narrowing orientation tuning width. Tuning curve properties for the different concentration of ACh: Individual neuron tuning curves before and after applying ACh. The tuning curves are shown for neurons with a preferred orientation of zero after applying ACh. (B) The gamma modulation in without-ACh pool is much stronger than in with-ACh pool. ACh clearly desynchronize in the gamma-frequency band. Shaded areas s.e.m. (C) Applying ACh to 15% of the inhibitory interneurons, through muscarinic receptors, leads to significant sharpening (Wilcoxon signed rank test; P < 0.01). Effect of applying ACh on the tuning curves of the individual neurons, with different levels of baseline activity of the network. (D) Applying ACh with high baseline activity and (E) low baseline activity of the network, strongly alters orientation selectivity of V1 neurons.