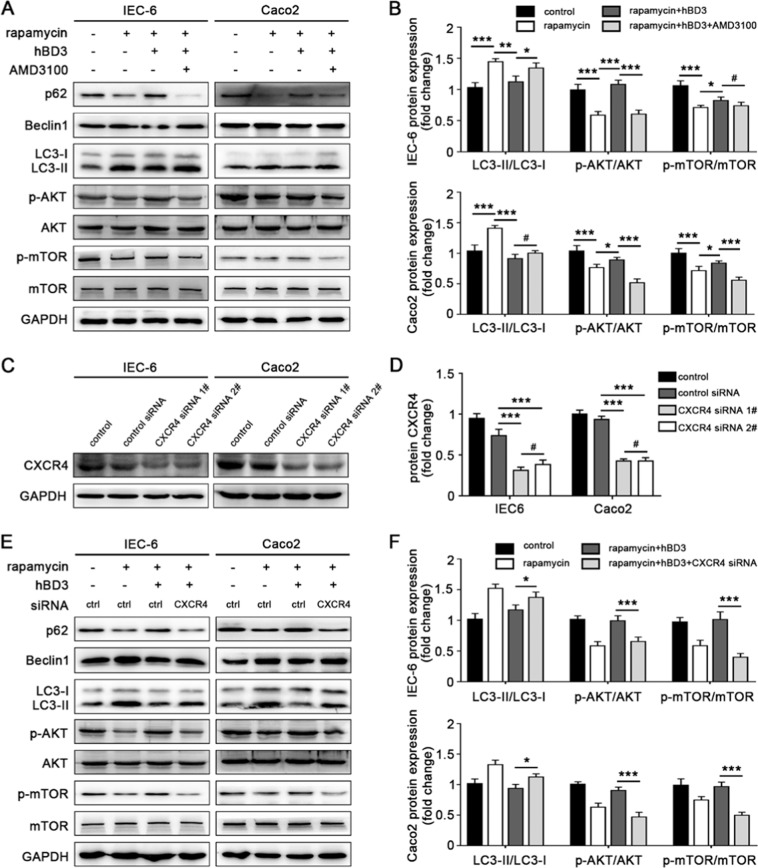
Figure 3.
CXCR4 signaling pathway was involved in hBD3-mediated autophagy suppression. Intestinal epithelial cells IEC-6 and Caco2 were incubated with CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3100 (10 μM, 24 h), and further treated with rapamycin (200 nM for IEC-6 or 50 Nm for Caco2, 24 h) and hBD3 (5 μg/ml, 12 h) as indicated. The expression of p62, Beclin1, LC3, p-mTOR and p-AKT in each group was assessed by western blotting (A) the LC3II/LC3I ratio and relative expression of p-mTOR and p-AKT were analyzed (B) with total mTOR and AKT as a loading control. CXCR4 knockdown efficiency was monitored (C) and analyzed (D) in IEC-6 and Caco2, respectively. After being incubated with CXCR4 siRNA for 36 h and treated with rapamycin and hBD3 mentioned above, cells in each group were lysed and subjected to western blotting using antibodies against p62, Beclin1, LC3, p-mTOR and p-AKT. (E) The LC3II/LC3I ratio and relative expression of p-mTOR and p-AKT were also analyzed (F) with the same methods referred to above. Data was displayed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, #p > 0.05.