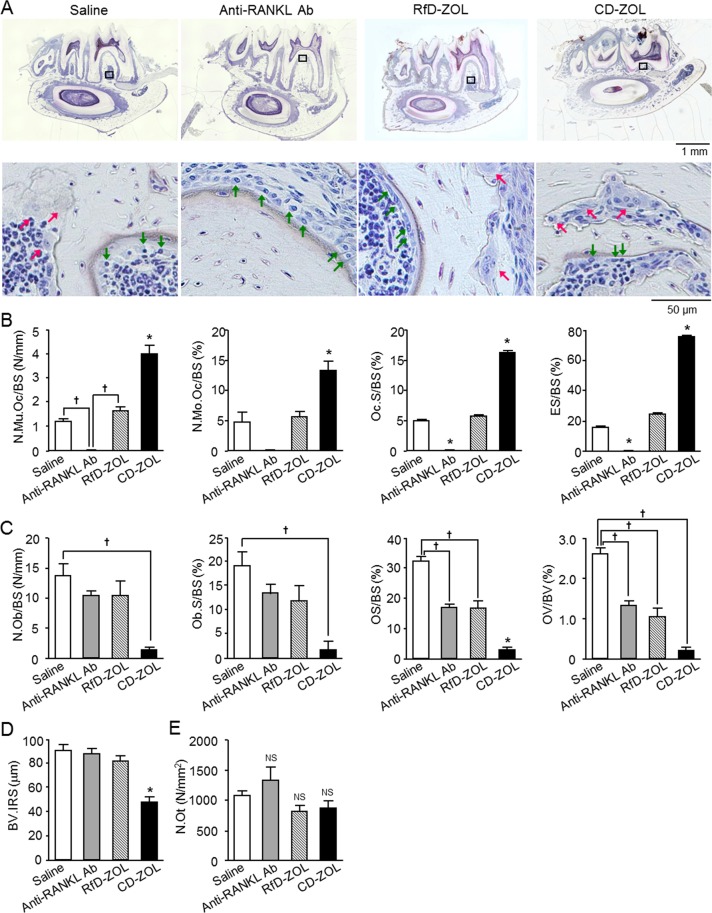
Figure 4.
Effects of long-term administrations of anti-RANKL antibody or zoledronic acid on mandibular alveolar bone. (A) Villanueva staining of mandibular alveolar bone of 8-week-old mice administered saline, anti-RANKL antibody (Ab) at 2.5 mg/kg, RfD-ZOL at 0.08 mg/kg, or CD-ZOL at 3.0 mg/kg weekly for 7 weeks. Higher magnification images of black-boxed regions in upper panels are shown in lower panels. Green arrows indicate osteoblasts and red arrows osteoclasts. Representative results are shown. (B–E) Mandibular alveolar bone static parameters were determined using bone morphometric analysis, including (B) number of multinucleated osteoclasts (N.Mu.Oc/BS), number of mononuclear osteoclasts (N.Mo.Oc/BS), osteoclast surface (Oc.S/BS), and eroded surface area (ES/BS) on the bone surface, (C) number of osteoblasts (N.Ob/BS), osteoblast surface (Ob.S/BS), osteoid surface area (OS/BS) on bone surface, and osteoid volume per bone volume (OV/BV), (D) bone volume of interradicular septum (BV.IRS), and (E) number of osteocytes (N.Ot). Four mice from each of the saline, anti-RANKL Ab, RfD-ZOL, and CD-ZOL groups were used. Statistical differences were assessed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer’s test. Statistically significant different from compared to *all the other groups, or †indicated groups, p < 0.05. Error bars represent SEM.