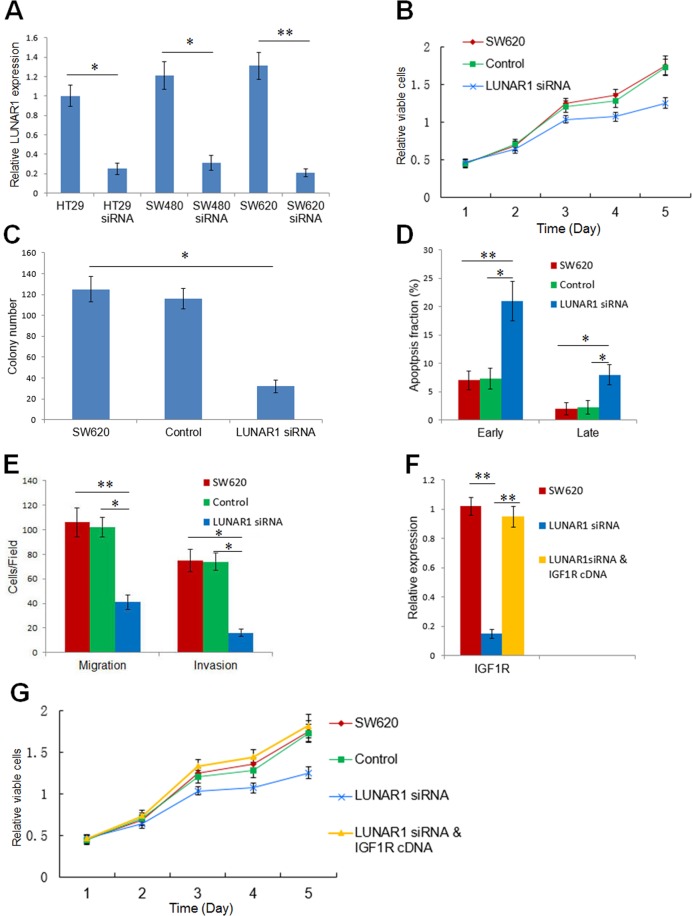
Figure 4.
Inhibition of LUNAR1 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via IGF1 signalling. (A) Downregulation of LUNAR1 by siRNA verified by real-time PCR. The relative expression of LUNAR1 was analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCt method. (B) The proliferation of cells detected by CCK-8 reagent. The data represent the results of three independent experiments. (C) Colony formation assay of three independent experiments. (D) The percentage of early apoptotic cells (Annexin V-positive and PI-negative) and late apoptotic cells (Annexin V-positive and PI-positive); the data represent the results of three independent experiments. (E) Migration and invasion assays; the counts of cells are presented as the mean values per field from at least five randomly-selected low-powered fields (×200) from three independent experiments (error bars: Means ± SDs). (F) IGF1R expression was decreased after LUNAR1 siRNA transfection, and increased after ectopically expressing vector containing IGF1R; (G) The proliferation of CRC cells detected by CCK-8 reagent indicated that ectopically IGF1R expression after LUNAR1 interference reversed the results of LUNAR1 siRNA transfection alone, the data represent the results of three independent experiments. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.001).