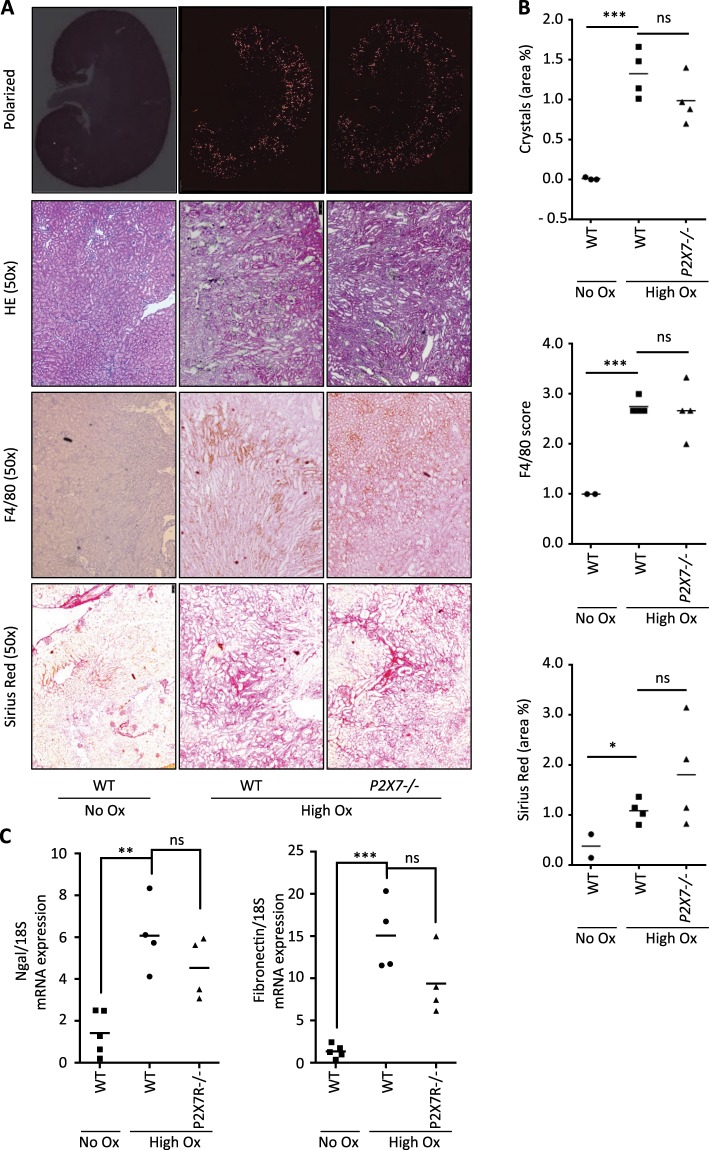
Figure 5.
P2X7−/− mice demonstrate similar amounts of renal crystal deposition and inflammation in vivo. WT and P2X7−/− mice were placed on a high soluble oxalate diet to induce renal failure. A separate group of WT mice received a control diet. (A,B) Whole kidney scans show no significant difference in crystal deposition, tubular damage, inflammation and renal fibrosis between WT and P2X7−/− mice on high oxalate diet. (C) mRNA levels of renal injury and fibrosis markers Ngal and fibronectin showing no significant difference between WT and P2X7−/− mice on high oxalate diet. Data are presented as mean. n = 3–4 animals. Statistical analysis for the histopathological evaluation (B) was performed using unpaired t-test. Statistical analysis for mRNA expression (C) was performed using one-way ANOVA. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant compared with mice on control diet (0% calcium/0% oxalate).