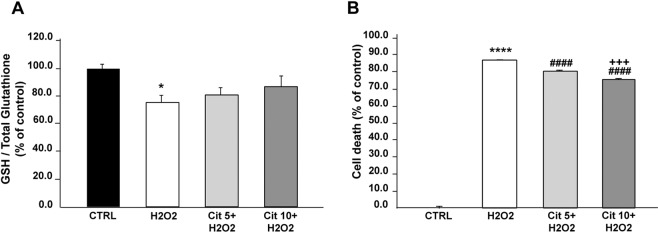
Figure 1.
Protective effect of Cit against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cell line. (A) Cit effect on intracellular oxidative stress (IOS). IOS was assessed by GSH/Total Glutathione ratio and expressed as % of control. GSH/Total glutathione ratio has been assessed in control conditions (CTRL), after oxidative stress induced by H2O2 500 µM (H2O2), after H2O2 500 µM in the presence of Cit 5 mM (Cit 5 + H2O2) or Cit 10 mM (Cit 10 + H2O2). The significant decrease in GSH/Total glutathione ratio is shown by* (*p < 0.03). (B) Cit effect on H2O2-induced cell death. Cell death has been assessed in control condition (CTRL), after treatment with H2O2 500 µM (H2O2) alone and in the presence of Cit 5 mM (Cit 5 + H2O2) or Cit 10 mM (Cit 10 + H2O2). The results are expressed as % of control. The significances are designed as followed: *: H2O2 vs CTRL; #: Cit + H2O2 vs H2O2; +: Cit10 + H2O2 vs Cit5 + H2O2. (****p < 0.0001; ####p < 0.0001; +++p = 0.0001). Data in A and B are presented as the mean ± SEM of 4 independent experiments.